Glucocorticoid use in acute respiratory failure from pulmonary causes and association with early changes in the systemic host immune response
- PMID: 38441708
- PMCID: PMC10914652
- DOI: 10.1186/s40635-024-00605-y
Glucocorticoid use in acute respiratory failure from pulmonary causes and association with early changes in the systemic host immune response
Abstract
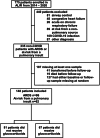
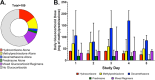
Background: Glucocorticoids are commonly used in patients with or at-risk for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), but optimal use remains unclear despite well-conducted clinical trials. We performed a secondary analysis in patients previously enrolled in the Acute Lung Injury and Biospecimen Repository at the University of Pittsburgh. The primary aim of our study was to investigate early changes in host response biomarkers in response to real-world use of glucocorticoids in patients with acute respiratory failure due to ARDS or at-risk due to a pulmonary insult. Participants had baseline plasma samples obtained on study enrollment and on follow-up 3 to 5 days later to measure markers of innate immunity (IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNFr1, ST2, fractalkine), epithelial injury (sRAGE), endothelial injury (angiopoietin-2), and host response to bacterial infections (procalcitonin, pentraxin-3). In our primary analyses, we investigated the effect of receiving glucocorticoids between baseline and follow-up samples on host response biomarkers measured at follow-up by doubly robust inverse probability weighting analysis. In exploratory analyses, we examined associations between glucocorticoid use and previously characterized host response subphenotypes (hyperinflammatory and hypoinflammatory).
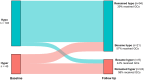
Results: 67 of 148 participants (45%) received glucocorticoids between baseline and follow-up samples. Dose and type of glucocorticoids varied. Regimens that used hydrocortisone alone were most common (37%), and median daily dose was equivalent to 40 mg methylprednisolone (interquartile range: 21, 67). Participants who received glucocorticoids were more likely to be female, to be on immunosuppressive therapy at baseline, and to have higher baseline levels of ST-2, fractalkine, IL-10, pentraxin-3, sRAGE, and TNFr1. Glucocorticoid use was associated with decreases in IL-6 and increases in fractalkine. In exploratory analyses, glucocorticoid use was more frequent in participants in the hyperinflammatory subphenotype (58% vs 40%, p = 0.05), and was not associated with subphenotype classification at the follow-up time point (p = 0.16).
Conclusions: Glucocorticoid use varied in a cohort of patients with or at-risk for ARDS and was associated with early changes in the systemic host immune response.
Keywords: ARDS; Cytokines; Glucocorticoids; Immune responses; Inflammation; Phenotypes; Pneumonia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Georgios Kitsios has received research funding from Karius, Inc., and Pfizer, Inc. Seyed Nouraie has received research funding from Pfizer, Inc. Bryan McVerry has received research funding from Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Synairgen, and BioAegis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Subphenotypes in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome treated with high-flow oxygen.Crit Care. 2023 Nov 1;27(1):419. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04687-0. Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 37915062 Free PMC article.
-
Trajectories of Host-Response Subphenotypes in Patients With COVID-19 Across the Spectrum of Respiratory Support.CHEST Crit Care. 2023 Dec;1(3):100018. doi: 10.1016/j.chstcc.2023.100018. Epub 2023 Sep 14. CHEST Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 38250011 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker-Based Classification of Patients With Acute Respiratory Failure Into Inflammatory Subphenotypes: A Single-Center Exploratory Study.Crit Care Explor. 2021 Aug 19;3(8):e0518. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000518. eCollection 2021 Aug. Crit Care Explor. 2021. PMID: 34476405 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids and acute lung injury.Crit Care Med. 2003 Apr;31(4 Suppl):S253-7. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000057900.19201.55. Crit Care Med. 2003. PMID: 12682449 Review.
-
Prolonged glucocorticoid treatment is associated with improved ARDS outcomes: analysis of individual patients' data from four randomized trials and trial-level meta-analysis of the updated literature.Intensive Care Med. 2016 May;42(5):829-840. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-4095-4. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Intensive Care Med. 2016. PMID: 26508525 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Is Prognostic of Mortality in Acute Respiratory Failure.Crit Care Explor. 2025 Mar 24;7(4):e1247. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000001247. eCollection 2025 Apr 1. Crit Care Explor. 2025. PMID: 40126931 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and biologic profiles of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome by prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or emphysema; a cohort study.Respir Res. 2024 Nov 8;25(1):400. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03027-2. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39516808 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

