Adult-Onset Still's Disease (AOSD): Advances in Understanding Pathophysiology, Genetics and Emerging Treatment Options
- PMID: 38441807
- PMCID: PMC10982104
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-024-01993-x
Adult-Onset Still's Disease (AOSD): Advances in Understanding Pathophysiology, Genetics and Emerging Treatment Options
Abstract
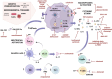
Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is a multisystemic complex disorder clinically characterised by episodes of spiking fever, evanescent rash, polyarthritis or diffuse arthralgias; multiorgan involvement may develop according to the hyper-inflammatory extent. The pathogenesis of AOSD is not completely recognised. The central role of macrophage activation, which results in T helper 1 (Th1) cell cytokine activation, is well established. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6 and IL-18 play a fundamental role in disease onset and progression. The disease may develop in both children and adults with overlapping clinical features, and although several subsets depending on the clinical manifestations and the cytokines expressed have been identified, the dichotomy between systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) and AOSD nowadays has been overcome, and the pathology is considered a disease continuum between ages. Various therapeutic approaches have been evaluated thus far, and different compounds are under assessment for AOSD treatment. Historically, glucocorticoids have been employed for treating systemic manifestations of Still's disease, while conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) demonstrated efficacy in controlling the articular manifestations. Currently, biological (b) DMARDs are widely employed; IL-1 inhibitors such as anakinra and canakinumab have proven to have high efficacy and an excellent safety profile and the anti-IL-6 tocilizumab is approved for sJIA, with several trials and longitudinal studies confirming its efficacy and safety. Moreover, in the light of the 'window of opportunity', new evidence showed that the earlier these treatments are initiated, the sooner clinical inactivity can be achieved. Other treatment options are being considered since several molecules involved in the disease pathophysiology can be targeted through various mechanisms. This review will provide a broad overview of AOSD pathophysiology, insights into specific organ manifestations and the currently available treatments with the identification of potential therapeutic targets involved in AOSD pathogenesis will be outlined.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Kudela H, Drynda S, Lux A, et al. Comparative study of Interleukin-18 (IL-18) serum levels in adult onset Still’s disease (AOSD) and systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) and its use as a biomarker for diagnosis and evaluation of disease activity. BMC Rheumatol. 2019;3:4. doi: 10.1186/s41927-019-0053-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

