Evaluation of molecular typing methods for some scab-causing Streptomyces strains from Turkey
- PMID: 38441818
- PMCID: PMC10914884
- DOI: 10.1007/s11274-024-03914-2
Evaluation of molecular typing methods for some scab-causing Streptomyces strains from Turkey
Abstract
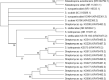
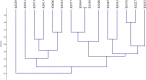
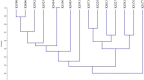
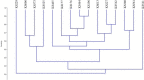
This study was conducted for identifying phylogenetic relationships between 15 scab-causing Streptomyces species including S. bottropensis, S. europaeiscabiei, S. scabiei, S. stelliscabiei and, other 11 Streptomyces sp. All of the strains were originally isolated from symptomatic potatoes in Erzurum Province, The Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey. Some morphological and biochemical properties of the strains were defined in our former research. Then, 16 s rRNA regions of them were sequenced. After the sequence data assembly, phylogenetic analyzes were performed. The phylogenetic analyses revealed that the strains are involved in the same major group and, substantially similar to reference strains. Additionally, some subgroup formations were also recorded. Moreover, Repetitive element-based PCR (Rep-PCR), Enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus (ERIC-PCR), and BOX-PCR fingerprinting molecular typing methods were used for as molecular typing methods. According to our knowledge, this is the first report on phylogenetic relationships of scab-causing Streptomyces species from Turkey. However, the identification of most pathogenic strains remained at the species level.
Keywords: 16S rRNA; BOX-PCR Streptomyces; Common-scab; ERIC-PCR; Phylogeny; Rep-PCR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Figures
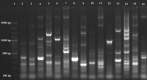
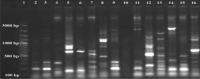
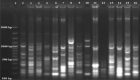
Similar articles
-
DNA relatedness among strains of Streptomyces pathogenic to potato in France: description of three new species, S. europaeiscabiei sp. nov. and S. stelliscabiei sp. nov. associated with common scab, and S. reticuliscabiei sp. nov. associated with netted scab.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000 Jan;50 Pt 1:91-99. doi: 10.1099/00207713-50-1-91. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10826791
-
Streptomyces brasiliscabiei, a new species causing potato scab in south Brazil.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2021 Jul;114(7):913-931. doi: 10.1007/s10482-021-01566-y. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2021. PMID: 33881637
-
HybProbes-based real-time PCR assay for specific identification of Streptomyces scabies and Streptomyces europaeiscabiei, the potato common scab pathogens.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016 Feb;62(2):153-9. doi: 10.1111/lam.12522. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26551004
-
Phylogenetic analysis of Streptomyces spp. causing potato scab based on 16S rRNA sequences.Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996 Apr;46(2):476-9. doi: 10.1099/00207713-46-2-476. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996. PMID: 8934906
-
Genetic and physiological determinants of Streptomyces scabies pathogenicity.Mol Plant Pathol. 2009 Sep;10(5):579-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00561.x. Mol Plant Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19694949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bencheikh M, Setti B. Characterizatıon of Streptomyces scabies isolated from common scab lesions on potato tubers by morphological, biochemical and pathogenicity tests in chlef region in western Algeria. Sci Technol. 2007;26:61–67.
-
- Bouchek-Mechiche K, Gardan NP, Jouan B. DNA relatedness among strains of Streptomyces pathogenic to potato in France: description of three new species, S. europaeiscabiei sp. nov, and S. stelliscabiei sp. nov associated with common scab, and S. reticuliscabiei sp nov associated with netted scab. Int J Syst Evol. 2000;50:91–99. doi: 10.1099/00207713-50-1-91. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

