Lipid-Binding Regions within PKC-Related Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase N1 (PKN1) Required for Its Regulation
- PMID: 38441874
- PMCID: PMC10956426
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00009
Lipid-Binding Regions within PKC-Related Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase N1 (PKN1) Required for Its Regulation
Abstract
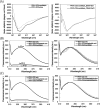
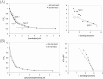
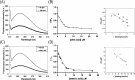
PKC-related serine/threonine protein kinase N1 (PKN1) is a protease/lipid-activated protein kinase that acts downstream of the RhoA and Rac1 pathways. PKN1 comprises unique regulatory, hinge region, and PKC homologous catalytic domains. The regulatory domain harbors two homologous regions, i.e., HR1 and C2-like. HR1 consists of three heptad repeats (HR1a, HR1b, and HR1c), with PKN1-(HR1a) hosting an amphipathic high-affinity cardiolipin-binding site for phospholipid interactions. Cardiolipin and C18:1 oleic acid are the most potent lipid activators of PKN1. PKN1-(C2) contains a pseudosubstrate sequence overlapping that of C20:4 arachidonic acid. However, the cardiolipin-binding site(s) within PKN1-(C2) and the respective binding properties remain unclear. Herein, we reveal (i) that the primary PKN1-(C2) sequence contains conserved amphipathic cardiolipin-binding motif(s); (ii) that trimeric PKN1-(C2) predominantly adopts a β-stranded conformation; (iii) that two distinct types of cardiolipin (or phosphatidic acid) binding occur, with the hydrophobic component playing a key role at higher salt levels; (iv) the multiplicity of C18 fatty acid binding to PKN1-(C2); and (v) the relevance of our lipid-binding parameters for PKN1-(C2) in terms of kinetic parameters previously determined for the full-length PKN1 enzyme. Thus, our discoveries create opportunities to design specific mammalian cell inhibitors that disrupt the localization of membrane-associated PKN1 signaling molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characterization of the novel cardiolipin binding regions identified on the protease and lipid activated PKC-related kinase 1.Protein Sci. 2019 Aug;28(8):1473-1486. doi: 10.1002/pro.3663. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Protein Sci. 2019. PMID: 31125460 Free PMC article.
-
Differential binding of RhoA, RhoB, and RhoC to protein kinase C-related kinase (PRK) isoforms PRK1, PRK2, and PRK3: PRKs have the highest affinity for RhoB.Biochemistry. 2013 Nov 12;52(45):7999-8011. doi: 10.1021/bi401216w. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 24128008
-
Protein Kinase C-Related Kinase (PKN/PRK). Potential Key-Role for PKN1 in Protection of Hypoxic Neurons.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2014 May;12(3):213-8. doi: 10.2174/1570159X11666131225000518. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24851086 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling by protein kinase C isoforms in the heart.Mol Cell Biochem. 1996 Apr 12-26;157(1-2):65-72. doi: 10.1007/BF00227882. Mol Cell Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8739230 Review.
-
The role of C2 domains in PKC signaling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;740:663-83. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-2888-2_29. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22453964 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

