Expression of bond-related behaviors affects titi monkey responsiveness to oxytocin and vasopressin treatments
- PMID: 38442081
- PMCID: PMC11830493
- DOI: 10.1111/nyas.15119
Expression of bond-related behaviors affects titi monkey responsiveness to oxytocin and vasopressin treatments
Abstract
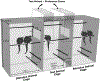
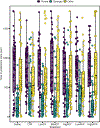
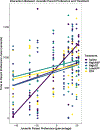
Social bonds influence physiology and behavior, which can shape how individuals respond to physical and affective challenges. Coppery titi monkey (Plecturocebus cupreus) offspring form selective bonds with their fathers, making them ideal for investigating how father-daughter bonds influence juveniles' responses to oxytocin (OT) and arginine-vasopressin (AVP) manipulations. We quantified the expression of father-daughter bond-related behaviors in females (n = 10) and gave acute intranasal treatments of saline, low/medium/high OT, low/high AVP, or an OT receptor antagonist (OTA) to subjects prior to a parent preference test. While females spent more time in proximity to their parents than strangers, we found a large degree of individual variation. Females with greater expression of bonding behaviors responded to OT treatments in a dose-dependent manner. Subjects also spent less time in proximity to strangers when treated with High OT (p = 0.003) and Low OT (p = 0.007), but more time when treated with High AVP (p = 0.007), Low AVP (p = 0.009), and OTA (p = 0.001). Findings from the present study suggest that variation in the expression of bond-related behaviors may alter responsiveness to OT and AVP, increasing engagement with unfamiliar social others. This enhanced sociality with strangers may promote the formation of pair bonds with partners.
Keywords: early‐life experience; intranasal oxytocin; intranasal vasopressin; nonhuman primate; preference test; proximity maintenance; social bond.
© 2024 The Authors. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The New York Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
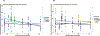
Similar articles
-
Titi monkey father-daughter bond-related behaviors explain stress response variability.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2023 Nov;157:106362. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2023.106362. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37586274 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal oxytocin does not change partner preference in female titi monkeys (Plecturocebus cupreus), but intranasal vasopressin decreases it.J Neuroendocrinol. 2023 Oct;35(10):e13339. doi: 10.1111/jne.13339. Epub 2023 Sep 13. J Neuroendocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37705310 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal vasopressin affects pair bonding and peripheral gene expression in male Callicebus cupreus.Genes Brain Behav. 2011 Apr;10(3):375-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2010.00677.x. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Genes Brain Behav. 2011. PMID: 21255269 Free PMC article.
-
The role of oxytocin and vasopressin in emotional and social behaviors.Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;124:53-68. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-59602-4.00004-6. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25248579 Review.
-
Cross-talk among oxytocin and arginine-vasopressin receptors: Relevance for basic and clinical studies of the brain and periphery.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2018 Oct;51:14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2017.10.004. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29054552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conserved and differing functions of the endocrine system across different social systems - oxytocin as a case study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 11;15:1418089. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1418089. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39055053 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lim MM & Young LJ. 2006. Neuropeptidergic regulation of affiliative behavior and social bonding in animals. Horm. Behav 50: 506–517. - PubMed
-
- Bales KL, Ardekani CS, Baxter A, et al. 2021. What is a pair bond? Horm. Behav 136: 105062. - PubMed
-
- Uchino BN 2006. Social support and health: a review of physiological processes potentially underlying links to disease outcomes. J. Behav. Med 29: 377–387. - PubMed
-
- Braiker HB & Kelley HH. 1979. Conflict in the development of close relationships. In Social exchange in developing relationships Burgess. & Houston T, Eds. 135–168. New York: Academic Press.
-
- Markey CN, Markey PM & Gray HF. 2007. Romantic Relationships and Health : An Examination of Individuals ‘ Perceptions of their Romantic Partners ‘ Influences on their Health. Sex Roles. 57: 435–445.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

