Recent Outcomes of Surgical Redo Aortic Valve Replacement in Prosthetic Valve Failure
- PMID: 38442916
- PMCID: PMC12115537
- DOI: 10.1055/a-2281-1897
Recent Outcomes of Surgical Redo Aortic Valve Replacement in Prosthetic Valve Failure
Abstract
Background: As redo surgical aortic valve replacement (AVR) is relatively high risk, valve-in-valve transcatheter AVR has emerged as an alternative for failed prostheses. However, the majority of studies are outdated. This study assessed the current clinical outcomes of redo AVR.
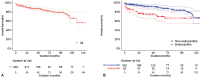
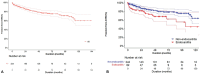
Methods and results: This study enrolled 324 patients who underwent redo AVR due to prosthetic valve failure from 2010 to 2021 in four tertiary centers. The primary outcome was operative mortality. The secondary outcomes were overall survival, cardiac death, and aortic valve-related events. Logistic regression analysis, clustered Cox proportional hazards models, and competing risk analysis were used to evaluate the independent risk factors. Redo AVR was performed in 242 patients without endocarditis and 82 patients with endocarditis. Overall operative mortality was 4.6% (15 deaths). Excluding patients with endocarditis, the operative mortality of redo AVR decreased to 2.5%. Multivariate analyses demonstrated that endocarditis (hazard ratio [HR]: 3.990, p = 0.014), longer cardiopulmonary bypass time (HR: 1.006, p = 0.037), and lower left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (HR: 0.956, p = 0.034) were risk factors of operative mortality. Endocarditis and lower LVEF were independent predictors of overall survival.
Conclusion: The relatively high risk of redo AVR was due to reoperation for prosthetic valve endocarditis. The outcomes of redo AVR for nonendocarditis are excellent. Our findings suggest that patients without endocarditis, especially with acceptable LVEF, can be treated safely with redo AVR.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Undergoing 3 Aortic Valve Interventions: The THIRD Multicenter Registry.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2025 Jan 13;18(1):103-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2024.10.037. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2025. PMID: 39814484
-
Rationale and Design of the REPEAT Trial: A Multicenter Randomized Trial Comparing Redo Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement to Valve-in-Valve Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 May 20;14(10):e040954. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.125.040954. Epub 2025 May 15. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40371620 Free PMC article.
-
Early Stroke Volume Variation After Transcatheter or Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Predicts Clinical Outcomes in Low-Flow Aortic Stenosis.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2025 Aug;106(2):1012-1022. doi: 10.1002/ccd.31654. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2025. PMID: 40457610 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of mortality after aortic valve replacement.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2007 Sep;32(3):469-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2007.06.012. Epub 2007 Jul 19. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2007. PMID: 17658266
-
Limited versus full sternotomy for aortic valve replacement.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 10;4(4):CD011793. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011793.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Dec 6;12:CD011793. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011793.pub3. PMID: 28394022 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Midterm Outcomes of Graft Insertion Technique for Redo Aortic Root Surgery.Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2025;31(1):25-00047. doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.25-00047. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2025. PMID: 40634068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davierwala P M, Borger M A, David T E, Rao V, Maganti M, Yau T M. Reoperation is not an independent predictor of mortality during aortic valve surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;131(02):329–335. - PubMed
-
- Onorati F, Biancari F, De Feo Met al.Mid-term results of aortic valve surgery in redo scenarios in the current practice: results from the multicentre European RECORD (REdo Cardiac Operation Research Database) initiative Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 20154702269–280., discussion 280 - PubMed
-
- Leontyev S, Borger M A, Davierwala P et al.Redo aortic valve surgery: early and late outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;91(04):1120–1126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

