Diagnostic accuracy of magnetically guided capsule endoscopy with a detachable string for detecting oesophagogastric varices in adults with cirrhosis: prospective multicentre study
- PMID: 38443074
- PMCID: PMC10912951
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj-2023-078581
Diagnostic accuracy of magnetically guided capsule endoscopy with a detachable string for detecting oesophagogastric varices in adults with cirrhosis: prospective multicentre study
Abstract
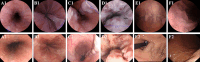
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy and safety of using magnetically guided capsule endoscopy with a detachable string (ds-MCE) for detecting and grading oesophagogastric varices in adults with cirrhosis.
Design: Prospective multicentre diagnostic accuracy study.
Setting: 14 medical centres in China.
Participants: 607 adults (>18 years) with cirrhosis recruited between 7 January 2021 and 25 August 2022. Participants underwent ds-MCE (index test), followed by oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD, reference test) within 48 hours. The participants were divided into development and validation cohorts in a ratio of 2:1.
Main outcome measures: The primary outcomes were the sensitivity and specificity of ds-MCE in detecting oesophagogastric varices compared with OGD. Secondary outcomes included the sensitivity and specificity of ds-MCE for detecting high risk oesophageal varices and the diagnostic accuracy of ds-MCE for detecting high risk oesophagogastric varices, oesophageal varices, and gastric varices.
Results: ds-MCE and OGD examinations were completed in 582 (95.9%) of the 607 participants. Using OGD as the reference standard, ds-MCE had a sensitivity of 97.5% (95% confidence interval 95.5% to 98.7%) and specificity of 97.8% (94.4% to 99.1%) for detecting oesophagogastric varices (both P<0.001 compared with a prespecified 85% threshold). When using the optimal 18% threshold for luminal circumference of the oesophagus derived from the development cohort (n=393), the sensitivity and specificity of ds-MCE for detecting high risk oesophageal varices in the validation cohort (n=189) were 95.8% (89.7% to 98.4%) and 94.7% (88.2% to 97.7%), respectively. The diagnostic accuracy of ds-MCE for detecting high risk oesophagogastric varices, oesophageal varices, and gastric varices was 96.3% (92.6% to 98.2%), 96.9% (95.2% to 98.0%), and 96.7% (95.0% to 97.9%), respectively. Two serious adverse events occurred with OGD but none with ds-MCE.
Conclusion: The findings of this study suggest that ds-MCE is a highly accurate and safe diagnostic tool for detecting and grading oesophagogastric varices and is a promising alternative to OGD for screening and surveillance of oesophagogastric varices in patients with cirrhosis.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03748563.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/disclosure-of-interest/ and declare: support from the “Ten Thousand Plan”-National High-Level Talents Special Support Plan and Shanghai Municipal Hospital Emerging Frontier Technology Joint Project for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


Comment in
-
Novel capsule endoscopy for detecting varices.BMJ. 2024 Mar 5;384:q506. doi: 10.1136/bmj.q506. BMJ. 2024. PMID: 38443073 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
