Projection of diabetes morbidity and mortality till 2045 in Indonesia based on risk factors and NCD prevention and control programs
- PMID: 38443384
- PMCID: PMC10914682
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54563-2
Projection of diabetes morbidity and mortality till 2045 in Indonesia based on risk factors and NCD prevention and control programs
Abstract
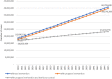
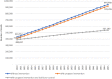
Diabetes Mellitus is one of the biggest health problems in Indonesia but the research on the disease's projection is still limited. This study aimed to make a projection model of prevalence and mortality of diabetes in Indonesia based on risk factors and NCD programs. The study was a quantitative non-experimental study through multiple linear regression models and system dynamics. The baseline projection was created by 2018 data and projections until 2045 involved the dynamization of risk factors and programs, population, and case fatality rate. The model was created from 205 districts data. This study used secondary data from Basic Health Research, BPJS Kesehatan, NCD programs, and Ministry of Health. The prevalence of diabetes in Indonesia is estimated to increase from 9.19% in 2020 (18.69 million cases) to 16.09% in 2045 (40.7 million cases). The prevalence will be lower to 15.68% (39.6 million) if interventions of programs were carried out, and to 9.22% (23.2 million) if the programs were added with prevention of risk factors. The projected number of deaths due to diabetes increases from 433,752 in 2020 to 944,468 in 2045. Deaths due to stroke among diabetes increases from 52,397 to 114,092 in the same period. Deaths from IHD among diabetes increase from 35,351 to 76,974, and deaths from chronic kidney disease among diabetes increase from 29,061 to 63,279. Diabetes prevalence and mortality in Indonesia rise significantly in Indonesia and can be reduced by intervention of several programs and risk factors. This study findings could be source of planning and evaluation of Diabetes prevention and control program at national and provincial level in the future related to risk factors control and program development.
Keywords: Diabetes; Mortality; Prevalence; Projection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- IHME. Burden of Disease, 2019. Available at https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/ (2020).
-
- Kemenkes RI. Report on result of national basic health research (Riskesdas) 2007. Available at https://repository.badankebijakan.kemkes.go.id/id/eprint/4386/1/Report%2... (2008).
-
- Kemenkes RI. Laporan Nasional Riset Kesehatan Dasar (Riskesdas) 2013. Available at https://repository.badankebijakan.kemkes.go.id/id/eprint/4467/1/Laporan_... (2013).
-
- Kemenkes RI. Laporan Nasional Riset Kesehatan Dasar (Riskesdas) 2018. Available at https://repository.badankebijakan.kemkes.go.id/id/eprint/3514/1/Laporan%... (2019).
-
- WHO . Summary Surveillance of Risk Factors for Noncommunicable Diseases The WHO STEPwise Approach. Geneva; 2001.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

