Distinct pathways drive anterior hypoblast specification in the implanting human embryo
- PMID: 38443567
- PMCID: PMC10940163
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-024-01367-1
Distinct pathways drive anterior hypoblast specification in the implanting human embryo
Abstract
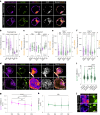
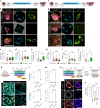
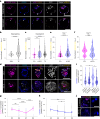
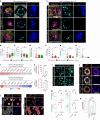
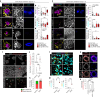
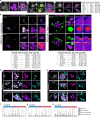
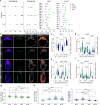
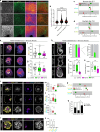
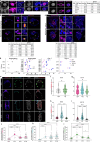
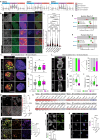
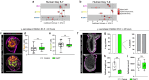
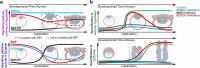
Development requires coordinated interactions between the epiblast, which generates the embryo proper; the trophectoderm, which generates the placenta; and the hypoblast, which forms both the anterior signalling centre and the yolk sac. These interactions remain poorly understood in human embryogenesis because mechanistic studies have only recently become possible. Here we examine signalling interactions post-implantation using human embryos and stem cell models of the epiblast and hypoblast. We find anterior hypoblast specification is NODAL dependent, as in the mouse. However, while BMP inhibits anterior signalling centre specification in the mouse, it is essential for its maintenance in human. We also find contrasting requirements for BMP in the naive pre-implantation epiblast of mouse and human embryos. Finally, we show that NOTCH signalling is important for human epiblast survival. Our findings of conserved and species-specific factors that drive these early stages of embryonic development highlight the strengths of comparative species studies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Molè, M. A., Weberling, A. & Zernicka-Goetz, M. in Current Topics in Developmental Biology Vol. 136 113–138 (Academic Press, 2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

