Dulaglutide treatment reverses depression-like behavior and hippocampal metabolomic homeostasis in mice exposed to chronic mild stress
- PMID: 38444330
- PMCID: PMC10915471
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.3448
Dulaglutide treatment reverses depression-like behavior and hippocampal metabolomic homeostasis in mice exposed to chronic mild stress
Abstract
Introduction: Treatment strategies for depression based on interventions for glucose and lipid metabolism disorders are receiving increasing attention. Investigating the mechanism of their antidepressant effect and exploring new diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers have attracted increasing attention. Dulaglutide, a long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonist, has been reported to alleviate cognitive deficits and neuronal damage. However, the antidepressant effect of dulaglutide and, especially, the underlying mechanism are still poorly understood. In this study, we aimed to explore the underlying biomarkers of depression and potential modulatory targets of dulaglutide in chronic mild stress (CMS) mice.
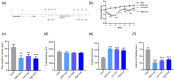
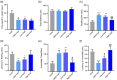
Methods: Sixty mice were randomly divided into a control group (CON group), a CMS+Vehicle group (CMS+Veh group), a CMS+0.3 mg/kg dulaglutide group (Low Dula group), and a CMS+0.6 mg/kg dulaglutide group (High Dula group). Numerous behavioral tests, mainly the open field test, forced swimming test, and tail suspension test, were applied to evaluate the potential effect of dulaglutide treatment on anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in mice exposed to chronic stress. Furthermore, a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approach was utilized to investigate the associated mechanisms of dulaglutide treatment.
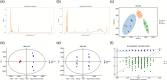
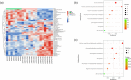
Results: Three weeks of dulaglutide treatment significantly reversed depressive-like but not anxiety-like behaviors in mice exposed to chronic stress for 4 weeks. The results from the metabolomics analysis showed that a total of 20 differentially expressed metabolites were identified between the CON and CMS+Veh groups, and 46 metabolites were selected between the CMS+Veh and High Dula groups in the hippocampus of the mice. Comprehensive analysis indicated that lipid metabolism, amino acid metabolism, energy metabolism, and tryptophan metabolism were disrupted in model mice that experienced depression and underwent dulaglutide therapy.
Conclusion: The antidepressant effects of dulaglutide in a CMS depression model were confirmed. We identified 64 different metabolites and four major pathways associated with metabolic pathophysiological processes. These primary data provide a new perspective for understanding the antidepressant-like effects of dulaglutide and may facilitate the use of dulaglutide as a potential therapeutic strategy for depression.
Keywords: depression; dulaglutide; liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; metabolomics.
© 2024 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Durability of protective effect of dulaglutide on pancreatic β-cells in diabetic mice: GLP-1 receptor expression is not reduced despite long-term dulaglutide exposure.Diabetes Metab. 2018 Jun;44(3):250-260. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2017.10.007. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Diabetes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29525225
-
Metabolomics analysis of the antidepressant prescription Danzhi Xiaoyao Powder in a rat model of Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress (CUMS).J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;260:112832. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112832. Epub 2020 May 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32387465
-
Long-Term Activation of Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor by Dulaglutide Prevents Diabetic Heart Failure and Metabolic Remodeling in Type 2 Diabetes.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Oct 4;11(19):e026728. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.026728. Epub 2022 Sep 29. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 36172969 Free PMC article.
-
Dulaglutide: the newest GLP-1 receptor agonist for the management of type 2 diabetes.Ann Pharmacother. 2015 Mar;49(3):351-9. doi: 10.1177/1060028014564180. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Ann Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 25565404 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a comprehensive review of the dulaglutide clinical data focusing on the AWARD phase 3 clinical trial program.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016 Nov;32(8):776-790. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2810. Epub 2016 May 15. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016. PMID: 27102969 Review.
References
-
- An, J. R. , Su, J. N. , Sun, G. Y. , Wang, Q. F. , Fan, Y. D. , Jiang, N. , Yang, Y. F. , & Shi, Y. (2022). Liraglutide alleviates cognitive deficit in db/db mice: Involvement in oxidative stress, iron overload, and ferroptosis. Neurochemical Research, 47(2), 279–294. 10.1007/s11064-021-03442-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cao, X. , Li, L. P. , Wang, Q. , Wu, Q. , Hu, H. H. , Zhang, M. , Fang, Y. Y. , Zhang, J. , Li, S. J. , Xiong, W. C. , Yan, H. C. , Gao, Y. B. , Liu, J. H. , Li, X. W. , Sun, L. R. , Zeng, Y. N. , Zhu, X. H. , & Gao, T. M. (2013). Astrocyte‐derived ATP modulates depressive‐like behaviors. Nature Medicine, 19(6), 773–777. 10.1038/nm.3162 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

