A comparative analysis of intravenous infusion methods for low-resource environments
- PMID: 38444409
- PMCID: PMC10912611
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1326144
A comparative analysis of intravenous infusion methods for low-resource environments
Abstract
Introduction: Intravenous (IV) therapy is a crucial aspect of care for the critically ill patient. Barriers to IV infusion pumps in low-resource settings include high costs, lack of access to electricity, and insufficient technical support. Inaccuracy of traditional drop-counting practices places patients at risk. By conducting a comparative assessment of IV infusion methods, we analyzed the efficacy of different devices and identified one that most effectively bridges the gap between accuracy, cost, and electricity reliance in low-resource environments.
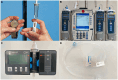
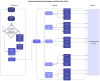
Methods: In this prospective mixed methods study, nurses, residents, and medical students used drop counting, a manual flow regulator, an infusion pump, a DripAssist, and a DripAssist with manual flow regulator to collect normal saline at goal rates of 240, 120, and 60 mL/h. Participants' station setup time was recorded, and the amount of fluid collected in 10 min was recorded (in milliliters). Participants then filled out a post-trial survey to rate each method (on a scale of 1 to 5) in terms of understandability, time consumption, and operability. Cost-effectiveness for use in low-resource settings was also evaluated.
Results: The manual flow regulator had the fastest setup time, was the most cost effective, and was rated as the least time consuming to use and the easiest to understand and operate. In contrast, the combination of the DripAssist and manual flow regulator was the most time consuming to use and the hardest to understand and operate.
Conclusion: The manual flow regulator alone was the least time consuming and easiest to operate. The DripAssist/Manual flow regulator combination increases accuracy, but this combination was the most difficult to operate. In addition, the manual flow regulator was the most cost-effective. Healthcare providers can adapt these devices to their practice environments and improve the safety of rate-sensitive IV medications without significant strain on electricity, time, or personnel resources.
Keywords: cost-effectiveness analysis; critically ill; global health disparities; intravenous infusion therapy; low-resource setting; sedation.
Copyright © 2024 Tomobi, Avoian, Ekwere, Waghmare, Diaban, Davis, Sy, Ogbonna, Streete, Aryee, Kulasingham and Sampson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IV DripAssist: An Innovative Way to Monitor Intravenous Infusions Away From an Outlet?Mil Med. 2019 Mar 1;184(Suppl 1):322-325. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usy365. Mil Med. 2019. PMID: 30901392
-
Flow rate accuracy of infusion devices within healthcare settings: a systematic review.Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2023 Jul 21;14:20420986231188602. doi: 10.1177/20420986231188602. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2023. PMID: 37492690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Gravity Intravenous Infusions in an Austere Environment Using the DripAssist Infusion Rate Monitor.AANA J. 2019 Feb;87(1):65-70. AANA J. 2019. PMID: 31587746
-
Comparison of accuracy and cost of disposable, nonmechanical pumps used for epidural infusions.Reg Anesth. 1997 May-Jun;22(3):260-6. doi: 10.1016/s1098-7339(06)80012-x. Reg Anesth. 1997. PMID: 9168219
-
A Systematic Review of Time and Resource Use Costs of Subcutaneous Versus Intravenous Administration of Oncology Biologics in a Hospital Setting.Pharmacoecon Open. 2023 Jan;7(1):3-36. doi: 10.1007/s41669-022-00361-3. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Pharmacoecon Open. 2023. PMID: 35996066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. (2022). Available at: https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed November 22, 2022.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

