Screening and Identification of DNA Nanostructure Aptamer Using the SELEX Method for Detection of Epsilon Toxin
- PMID: 38444705
- PMCID: PMC10912870
- DOI: 10.5812/ijpr-140505
Screening and Identification of DNA Nanostructure Aptamer Using the SELEX Method for Detection of Epsilon Toxin
Abstract
Background: Epsilon toxin (ETX), produced by Clostridium perfringens, is one of the most potent toxins known, with a lethal potency approaching that of botulinum neurotoxins. Epsilon toxin is responsible for enteritis. Therefore, the development of rapid and simple methods to detect ETX is imperative. Aptamers are single-stranded oligonucleotides that can bind tightly to specific target molecules with an affinity comparable to that of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). DNA aptamers can serve as tools for the molecular identification of organisms, such as pathogen subspecies.
Objectives: This study aimed to isolate high-affinity single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) aptamers against ETX.
Methods: This study identified aptamers using the Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (SELEX) method, enzyme-linked apta-sorbent assay (ELASA), and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) to determine the affinity and specificity of the newly obtained aptamers targeting ETX.
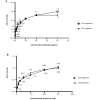
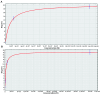
Results: Several aptamers obtained through the SELEX process were studied. Among them, 2 aptamers, ETX clone 3 (ETX3; dissociation constant (Kd = 8.4 ± 2.4E-9M) and ETX11 (Kd = 6.3 ± 1.3E-9M) had favorable specificity for ETX. The limits of detection were 0.21 and 0.08 μg/mL for ETX3 and ETX11, respectively..
Conclusions: The discovered aptamers can be used in various aptamer-based rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of ETX.
Keywords: Clostridium perfringens; DNA Aptamer; ELASA; Epsilon Toxin; SELEX; SPR.
Copyright © 2023, Shafiei et al.
Figures



References
-
- Xin W, Wang J. Clostridium perfringens epsilon toxin: Toxic effects and mechanisms of action. Biosafety Health. 2019;1(2):71–5.
-
- Seyer A, Fenaille F, Feraudet-Tarisse C, Volland H, Popoff MR, Tabet JC, et al. Rapid quantification of clostridial epsilon toxin in complex food and biological matrixes by immunopurification and ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2012;84(11):5103–9. doi: 10.1021/ac300880x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
