Function of KvLQT1 potassium channels in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 38444763
- PMCID: PMC10912346
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1345488
Function of KvLQT1 potassium channels in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
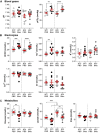
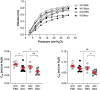
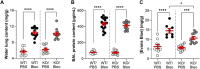
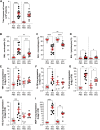
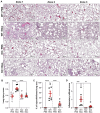
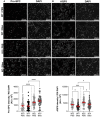
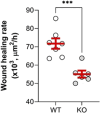
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is characterized by an exacerbated inflammatory response, severe damage to the alveolar-capillary barrier and a secondary infiltration of protein-rich fluid into the airspaces, ultimately leading to respiratory failure. Resolution of ARDS depends on the ability of the alveolar epithelium to reabsorb lung fluid through active transepithelial ion transport, to control the inflammatory response, and to restore a cohesive and functional epithelium through effective repair processes. Interestingly, several lines of evidence have demonstrated the important role of potassium (K+) channels in the regulation of epithelial repair processes. Furthermore, these channels have previously been shown to be involved in sodium/fluid absorption across alveolar epithelial cells, and we have recently demonstrated the contribution of KvLQT1 channels to the resolution of thiourea-induced pulmonary edema in vivo. The aim of our study was to investigate the role of the KCNQ1 pore-forming subunit of KvLQT1 channels in the outcome of ARDS parameters in a model of acute lung injury (ALI). We used a molecular approach with KvLQT1-KO mice challenged with bleomycin, a well-established ALI model that mimics the key features of the exudative phase of ARDS on day 7. Our data showed that KvLQT1 deletion exacerbated the negative outcome of bleomycin on lung function (resistance, elastance and compliance). An alteration in the profile of infiltrating immune cells was also observed in KvLQT1-KO mice while histological analysis showed less interstitial and/or alveolar inflammatory response induced by bleomycin in KvLQT1-KO mice. Finally, a reduced repair rate of KvLQT1-KO alveolar cells after injury was observed. This work highlights the complex contribution of KvLQT1 in the development and resolution of ARDS parameters in a model of ALI.
Keywords: acute lung injury; alveolar-capillary barrier; animal model; injury and repair; potassium channels; pulmonary inflammation; respiratory function.
Copyright © 2024 Aubin Vega, Girault, Meunier, Chebli, Privé, Robichaud, Adam and Brochiero.
Conflict of interest statement
At the time of the study, AR was employed by SCIREQ Scientific Respiratory Equipment Inc. (an emka TECHNOLOGIES company), a commercial entity with interests in a topic area related to the content of this article. AR had no decision-making role in the manuscript prior to its submission. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pro-Reparative Effects of KvLQT1 Potassium Channel Activation in a Mouse Model of Acute Lung Injury Induced by Bleomycin.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 7;26(15):7632. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157632. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806760 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of KvLQT1 potassium channel modulation on alveolar fluid homeostasis in an animal model of thiourea-induced lung edema.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1069466. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1069466. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36699692 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone fails to improve bleomycin-induced acute lung injury in mice.Physiol Rep. 2019 Nov;7(21):e14253. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14253. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31724341 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of mechanosensitive ion channels in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome.Respir Res. 2022 Dec 20;23(1):366. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02303-3. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 36539808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators Regulate Alveolar Fluid Clearance during Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Apr 20;131(8):982-989. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.229890. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 29664060 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex and disease regulate major histocompatibility complex class I expression in human lung epithelial cells.Physiol Rep. 2024 Sep;12(17):e70025. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70025. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39223101 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-Reparative Effects of KvLQT1 Potassium Channel Activation in a Mouse Model of Acute Lung Injury Induced by Bleomycin.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 7;26(15):7632. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157632. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806760 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in a murine model of acute lung injury.Exp Physiol. 2024 Jun;109(6):966-979. doi: 10.1113/EP091682. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Exp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38594909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam D., Bilodeau C., Sognigbé L., Maillé É., Ruffin M., Brochiero E. (2018). CFTR rescue with VX-809 and VX-770 favors the repair of primary airway epithelial cell cultures from patients with class II mutations in the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproducts. J. Cyst. Fibros. 17, 705–714. 10.1016/j.jcf.2018.03.010 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

