Understanding bacterial pathogenicity: a closer look at the journey of harmful microbes
- PMID: 38444801
- PMCID: PMC10912505
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1370818
Understanding bacterial pathogenicity: a closer look at the journey of harmful microbes
Abstract
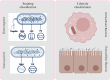
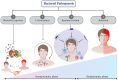
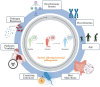
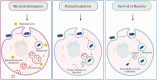
Bacteria are the most prevalent form of microorganisms and are classified into two categories based on their mode of existence: intracellular and extracellular. While most bacteria are beneficial to human health, others are pathogenic and can cause mild to severe infections. These bacteria use various mechanisms to evade host immunity and cause diseases in humans. The susceptibility of a host to bacterial infection depends on the effectiveness of the immune system, overall health, and genetic factors. Malnutrition, chronic illnesses, and age-related vulnerabilities are the additional confounders to disease severity phenotypes. The impact of bacterial pathogens on public health includes the transmission of these pathogens from healthcare facilities, which contributes to increased morbidity and mortality. To identify the most significant threats to public health, it is crucial to understand the global burden of common bacterial pathogens and their pathogenicity. This knowledge is required to improve immunization rates, improve the effectiveness of vaccines, and consider the impact of antimicrobial resistance when assessing the situation. Many bacteria have developed antimicrobial resistance, which has significant implications for infectious diseases and favors the survival of resilient microorganisms. This review emphasizes the significance of understanding the bacterial pathogens that cause this health threat on a global scale.
Keywords: AMR; bacteria; disease severity; host susceptibility; immune response.
Copyright © 2024 Soni, Sinha and Pandey.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emerging challenges in antimicrobial resistance: implications for pathogenic microorganisms, novel antibiotics, and their impact on sustainability.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 29;15:1403168. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1403168. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38741745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Children Reported by the ISPED Program in China, 2016 to 2020.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0028321. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00283-21. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34730410 Free PMC article.
-
Global geographic trends in antimicrobial resistance: the role of international travel.J Travel Med. 2019 Dec 23;26(8):taz036. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taz036. J Travel Med. 2019. PMID: 31115466 Review.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jul 5;11(13):1946. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11131946. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimates of antibiotic resistance in Italy and Western Europe in 2019: a MICROBE-based comparative analysis.Epidemiol Prev. 2024 Jan-Feb;48(1):48-59. doi: 10.19191/EP24.1.A648.020. Epidemiol Prev. 2024. PMID: 38482785 English.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Insights in infectious agents and disease: 2022.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 9;15:1443636. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1443636. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39044949 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Inflammasomes and Signaling Pathways: Key Mechanisms in the Pathophysiology of Sepsis.Cells. 2025 Jun 19;14(12):930. doi: 10.3390/cells14120930. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40558557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circumventing the Impossible: Cell-Free Synthesis of Protein Toxins for Medical and Diagnostic Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 11;25(24):13293. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413293. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress and Technological Application Prospects of Comprehensive Evaluation Methods for Egg Freshness.Foods. 2025 Apr 25;14(9):1507. doi: 10.3390/foods14091507. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant-Derived Antimicrobials and Their Crucial Role in Combating Antimicrobial Resistance.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Aug 9;13(8):746. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13080746. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39200046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

