Response of serum biochemical profile, antioxidant enzymes, and gut microbiota to dietary Hong-bailanshen supplementation in horses
- PMID: 38444806
- PMCID: PMC10912594
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1327210
Response of serum biochemical profile, antioxidant enzymes, and gut microbiota to dietary Hong-bailanshen supplementation in horses
Abstract
Background: Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is widely used in humans and animals, which is very important for health. TCM affects the body 's immunity and changes in intestinal flora. This study was conducted to investigate the effects of dietary Hong-bailanshen (HBLS) supplementation in horses on serum biochemical profile, antioxidant enzymes and gut microbiota.
Methods: In this study, five horses were selected. On day 0, 14, 28, blood samples and feces were collected on days 0, 14, and 28 to analyse gut microbiota, serum biochemical and redox indexes.
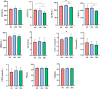
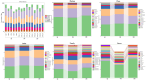
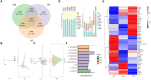
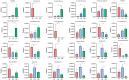
Results: The results showed that the addition of HBLS to horse diets significantly decreased the level of alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, creatine kinase and malondialdehyde (p < 0.05, p < 0.01) and significantly increased the activity of total antioxidant capacity, superoxide dismutase and catalase (p < 0.05, p < 0.01). Compared with day 14, the levels of alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase and creatine kinase were significantly decreased; however, the level of catalase was significantly increased in the horses continuously fed with HBLS for 28 days (p < 0.05, p < 0.01). Alpha diversity analysis was performed that chao1 (p < 0.05), observed_specicies, faith'pd and goods_coverage upregulated in the horses fed HBLS. A total of 24 differential genera were detected adding HBLS to diet increased the abundance of Bacillus, Lactobacillaceae, Leuconostocaceae, Christensenellaceae, Peptostreptococcaceae, Faecalibacterium, Erysipelotrichaceae, Pyramidobacter, Sphaerochaeta, WCHB1-25, Bacteria, Oscillospira, and Acetobacteraceae, while reduced Aerococcus, EtOH8, Syntrophomonas, Caulobacter, Bradyrhizobiaceae, W22, Succinivibrionaceae, and Desulfovibrio (p < 0.05, p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Adding HBLS to the diet could be a potentially effective strategy to improve horses' health.
Keywords: HBLS; antioxidant enzymes; biochemical profile; gut microbiota; horse.
Copyright © 2024 Ding, Gu, Meng, Hu, Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effect of dietary resveratrol supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, intestinal immunity and gut microbiota in yellow-feathered broilers challenged with lipopolysaccharide.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 25;13:977087. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.977087. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36090096 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota changes in horses with Chlamydia.BMC Microbiol. 2023 Sep 2;23(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02986-8. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37660043 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary supplementation of squalene increases the growth performance of early-weaned piglets by improving gut microbiota, intestinal barrier, and blood antioxidant capacity.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Nov 3;9:995548. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.995548. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36406080 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary supplementation with Dendrobium officinale leaves improves growth, antioxidant status, immune function, and gut health in broilers.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 18;14:1255894. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1255894. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37789853 Free PMC article.
-
Growth, Health, and Gut Microbiota of Female Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei Broodstock Fed Different Phospholipid Sources.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 10;11(6):1143. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061143. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold C., Pilla R., Chaffin K., Lidbury J., Steiner J., Suchodolski J. (2021). Alterations in the fecal microbiome and metabolome of horses with antimicrobial-associated diarrhea compared to antibiotic-treated and non-treated healthy case controls. Animals 11:1807. doi: 10.3390/ani11061807, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

