Application of JAK inhibitors in paradoxical reaction through immune-related dermatoses
- PMID: 38444845
- PMCID: PMC10912518
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1341632
Application of JAK inhibitors in paradoxical reaction through immune-related dermatoses
Abstract
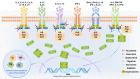
Biologics play a positive and effective role in the treatment of immune-related dermatoses. However, many other immune-related diseases have also manifested along with biologics treatment. Paradoxical reaction through immune-related dermatoses refer to the new onset or exacerbation of other immune-mediated dermatoses (mainly psoriasis and atopic dermatitis) after biologics treatment of inflammatory dermatoses (mainly psoriasis and atopic dermatitis), such as new atopic dermatitis (AD) in psoriasis (PsO) treatment and new PsO in AD treatment. A common genetic background and Inflammatory pathway are possible pathogenesis. Faced with paradoxical reactions, the choice of therapy needs to be directed toward therapies effective for both diseases, such as Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. The Janus kinase and signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway plays an important role in the inflammatory pathway, and has been widely used in the treatment of AD and PsO in recent years. This article focuses on JAK inhibitors such as tofacitinib, baricitinib, ruxolitinib, Abrocitinib, upadacitinib, and deucravacitinib, to explore the possible application in treatment of paradoxical reactions. Common side effects, baseline risk factors and safety use of JAK inhibitors were discussed.
Keywords: JAK inhibitors; atopic dermatitis; immune-related dermatoses; paradoxical reaction; psoriasis.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

