Balloon dilation of the eustachian tube using endovascular balloon under local anesthesia-a case series and systematic literature review
- PMID: 38444902
- PMCID: PMC10912332
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1271248
Balloon dilation of the eustachian tube using endovascular balloon under local anesthesia-a case series and systematic literature review
Abstract
Objective: To report a novel technique in Balloon Dilation of Eustachian Tube (BDET) using an endovascular balloon (EVB), in a prospective cohort. The results are compared with reported outcomes using standard balloons.
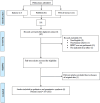
Methods: Demographic information and clinical parameters were collected prospectively fora series of patients with obstructive eustachian tube dysfunction (OETD). Balloon dilation Eustachian tuboplasty was performed under local anesthesia in a tertiary referral center, using the EVB. Systematic literature review was used for comparison, using Medline via "PubMed", "Embase", and "Web of Science".
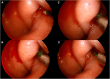
Results: Eight OETD candidates (12 ears) were enrolled; 5 males and 3 females. Average age was 48 (range -23 to 63) years. The most common presenting symptom was aural fullness (9/12), followed by ear pressure (7/12), hearing loss (5/12) and tinnitus (4/12). Otoscopically, tympanic membrane retraction was evident in 10/12 ears, the majority of which was class II-Sade classification. Pre-operative tympanogram was type B and C in 7 and 5 ears, respectively. All BDETs were performed without complications. Post-operative tympanometry was A in 8/12 ears. Post-operatively, Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire-7 results reduced to within normal limits (average score ≤3) in 11/12 ears (p = 0.0014). The systematic literature review included 6 papers (193 patients, 262 ETs) with comparable results, most also with little adverse effects.
Conclusion: BDET using an EVB is a safe and effective option for OETD. It is well tolerated under local anesthesia in properly selected individuals. The reduced procedural cost may be an important factor in certain healthcare jurisdictions.
Keywords: balloon dilation; endovascular balloon; endovascular catheter; eustachian tube; eustachian tube dysfunction; eustachian tuboplasty.
© 2024 Ungar, Demir Bajin, Dahm, Lin, Chen and Le.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Valsalva AM. De aure humana tractatus…Interposita est musculorum uvulae atque pharyngis nova descriptio. Pisarius; (1704).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

