Plasma microrna quantification protocol
- PMID: 38445249
- PMCID: PMC10914336
- DOI: 10.20517/2574-1209.2023.69
Plasma microrna quantification protocol
Abstract
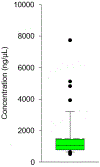
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules that regulate translation and are involved in many pathological processes. They have emerged as promising biomarkers for diagnosis of conditions such as aortic aneurysm disease. Quantifying miRNAs in plasma is uniquely challenging because of the lack of standardized reproducible protocols. To facilitate the independent verification of conclusions, it is necessary to provide a thorough disclosure of all pertinent experimental details. In this technical note, we present a comprehensive protocol for quantifying plasma miRNAs using droplet digital PCR. We detail the entire workflow, including blood collection, plasma processing, cryo-storage, miRNA isolation, reverse transcription, droplet generation, PCR amplification, fluorescence reading, and data analysis. We offer comprehensive guidance regarding optimization, assay conditions, expected results, and insight into the troubleshooting of common issues. The stepwise normalization and detailed methodological guide enhance reproducibility. Moreover, multiple portions of this protocol may be automated. The data provided in this technical note is demonstrative of the values typically obtained when following its steps. To facilitate standardization in data reporting, we include a table of expected aortic aneurysm-related miRNA levels in healthy human plasma. This versatile protocol can be easily adapted to quantify most circulating miRNAs in plasma, making it a valuable resource for diagnostic development.
Keywords: MicroRNA; aortic aneurysm; ddPCR; plasma; quantification.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

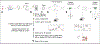

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
