Assessing the application of barbed sutures in comparison to conventional sutures for surgical applications: a global systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical animal studies
- PMID: 38445518
- PMCID: PMC11093437
- DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001230
Assessing the application of barbed sutures in comparison to conventional sutures for surgical applications: a global systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical animal studies
Abstract
Background: Following an initiative published by Lancet in 2002 and an IDEAL-D framework, the value of preclinical animal studies has garnered increasing attention in recent research. Numerous preclinical animal experiments tried to generate evidence to guide the development of barbed sutures. However, discernible drawbacks and incongruities in outcomes have emerged between clinical and preclinical animal studies. Therefore, this meta-analysis aimed to review the preclinical animal experiments comparing barbed sutures with conventional sutures. The authors hope to facilitate clinical translation of barbed sutures by evaluating effectiveness, safety, and physical properties/reliability.
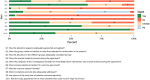
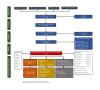
Materials and methods: A systematic search of PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov was conducted to identify controlled preclinical animal experiments comparing barbed sutures with conventional sutures. The risk of bias was assessed using SYRCLE. GRADE approach was used to evaluate evidence quality. Revman was applied to analyze all the data. Subgroup, sensitivity, and meta-regression analyses were also performed.
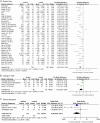
Results: A total of 62 articles were eligible with low to moderate quality, including 2158 samples from 10 different animal species across 27 surgical procedures. Barbed suture exhibited a significant reduction in suture time, limited change in Cross-Sectional Area (CSA), and decreased instances of tissue disruption (all P <0.05). Subgroup analyses, considering both clinical and research significance, indicated that barbed sutures might cause more specific adverse events and demonstrate suboptimal performance of physical properties/reliability. Meta-regression suggested that heterogeneity resulted from variations in studies and animal models.
Conclusion: Although barbed suture demonstrated superiority in numerous surgeries for time efficiency, its safety and physical properties/reliability might be influenced by diverse preclinical models, sutures' brand, surgeries, and anatomical sites. Further evaluation, based on standardized and well-designed animal experiments, is essential for medical device development and applications in human beings.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Effectiveness and safety of knotless barbed sutures in cosmetic surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2023 Dec;87:416-429. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2023.10.084. Epub 2023 Oct 13. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2023. PMID: 37939647
Cited by
-
Application of double-needle bi-direction barbed sutures in laparoscopic common bile duct suture: a propensity score matching analysis.Updates Surg. 2025 Jan 12. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02100-9. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 39800788
-
[Effectiveness analysis of channel-assisted minimally invasive repair technique combined with flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer for Achilles tendon sleeve avulsion].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Mar 15;39(3):264-270. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202412038. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40101899 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Barbed and Non-Barbed Suture Materials for Ventral Hernia Repair: An Experimental Study.J Clin Med. 2025 May 1;14(9):3139. doi: 10.3390/jcm14093139. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40364169 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Outcomes Among Patients Undergoing Open Abdominal or Orthopedic Surgery with Wound Closure Incorporating Triclosan-Coated Barbed Sutures: A Multi-Institutional, Retrospective Database Study.Med Devices (Auckl). 2025 Mar 6;18:161-176. doi: 10.2147/MDER.S508169. eCollection 2025. Med Devices (Auckl). 2025. PMID: 40071132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quill™ Synthetic Absorbable Barbed Suture. 510(k) Summary 2004. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf4/k042075.pdf.
-
- Lin Y, Long Y, Lai S, et al. . The effectiveness and safety of barbed sutures in the bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg 2019;29:1756–1764. - PubMed
-
- Rivero-Santana A, Perestelo-Perez L, Alvarez-Perez Y, et al. . Stepped care for the treatment of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord 2021;294:391–409. - PubMed
-
- Tulandi T, Einarsson JI. The use of barbed suture for laparoscopic hysterectomy and myomectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Minim Invasive Gynecol 2014;21:210–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

