Integrating network pharmacology and in silico analysis deciphers Withaferin-A's anti-breast cancer potential via hedgehog pathway and target network interplay
- PMID: 38446743
- PMCID: PMC10917074
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbae032
Integrating network pharmacology and in silico analysis deciphers Withaferin-A's anti-breast cancer potential via hedgehog pathway and target network interplay
Abstract
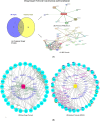
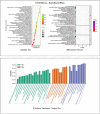
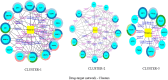
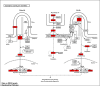
This study examines the remarkable effectiveness of Withaferin-A (WA), a withanolide obtained from Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha), in encountering the mortiferous breast malignancy, a global peril. The predominant objective is to investigate WA's intrinsic target proteins and hedgehog (Hh) pathway proteins in breast cancer targeting through the application of in silico computational techniques and network pharmacology predictions. The databases and webtools like Swiss target prediction, GeneCards, DisGeNet and Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man were exploited to identify the common target proteins. The culmination of the WA network and protein-protein interaction network were devised using Stitch and String web tools, through which the drug-target network of 30 common proteins was constructed employing Cytoscape-version 3.9. Enrichment analysis was performed by incorporating Gprofiler, Metascape and Cytoscape plugins. David compounded the Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, and enrichment was computed through bioinformatics tools. The 20 pivotal proteins were docked harnessing Glide, Schrodinger Suite 2023-2. The investigation was governed by docking scores and affinity. The shared target proteins underscored the precise Hh and WA network roles with the affirmation enrichment P-value of <0.025. The implications for hedgehog and cancer pathways were profound with enrichment (P < 0.01). Further, the ADMET and drug-likeness assessments assisted the claim. Robust interactions were noticed with docking studies, authenticated through molecular dynamics, molecular mechanics generalized born surface area scores and bonds. The computational investigation emphasized WA's credible anti-breast activity, specifically with Hh proteins, implying stem-cell-level checkpoint restraints. Rigorous testament is imperative through in vitro and in vivo studies.
Keywords: in silico studies; breast cancer; computational analysis; hedgehog pathway; network pharmacology; phytoconstituents.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures







References
-
- Giaquinto AN, Sung H, Miller KD, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 2022;72(6):524–41. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 2023;73(1):17–48. - PubMed
-
- Chhikara BS, Parang K. Global cancer statistics 2022: the trends projection analysis. Chem Biol Lett 2023;10(1):451 https://pubs.thesciencein.org/cbl.
-
- Ravi L, Sreenivas BKA, Kumari GRS, Archana O. Anticancer cytotoxicity and antifungal abilities of green-synthesized cobalt hydroxide (co(OH)2) nanoparticles using Lantana camara L. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 2022;11(1):1–14.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

