Deep learning model for personalized prediction of positive MRSA culture using time-series electronic health records
- PMID: 38448409
- PMCID: PMC10917736
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46211-0
Deep learning model for personalized prediction of positive MRSA culture using time-series electronic health records
Abstract
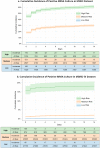
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) poses significant morbidity and mortality in hospitals. Rapid, accurate risk stratification of MRSA is crucial for optimizing antibiotic therapy. Our study introduced a deep learning model, PyTorch_EHR, which leverages electronic health record (EHR) time-series data, including wide-variety patient specific data, to predict MRSA culture positivity within two weeks. 8,164 MRSA and 22,393 non-MRSA patient events from Memorial Hermann Hospital System, Houston, Texas are used for model development. PyTorch_EHR outperforms logistic regression (LR) and light gradient boost machine (LGBM) models in accuracy (AUROCPyTorch_EHR = 0.911, AUROCLR = 0.857, AUROCLGBM = 0.892). External validation with 393,713 patient events from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC)-IV dataset in Boston confirms its superior accuracy (AUROCPyTorch_EHR = 0.859, AUROCLR = 0.816, AUROCLGBM = 0.838). Our model effectively stratifies patients into high-, medium-, and low-risk categories, potentially optimizing antimicrobial therapy and reducing unnecessary MRSA-specific antimicrobials. This highlights the advantage of deep learning models in predicting MRSA positive cultures, surpassing traditional machine learning models and supporting clinicians' judgments.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Rybak M, et al. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin in adult patients: a consensus review of the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2009;66:82–98. doi: 10.2146/ajhp080434. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carey GB, et al. Estimated mortality with early empirical antibiotic coverage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in hospitalized patients with bacterial infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023;78:1150–1159. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkad078. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

