Emerging roles of SIRT1 activator, SRT2104, in disease treatment
- PMID: 38448466
- PMCID: PMC10917792
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-55923-8
Emerging roles of SIRT1 activator, SRT2104, in disease treatment
Abstract
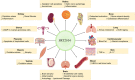
Silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) is a NAD+-dependent class III deacetylase that plays important roles in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases, positioning it as a prime candidate for therapeutic intervention. Among its modulators, SRT2104 emerges as the most specific small molecule activator of SIRT1, currently advancing into the clinical translation phase. The primary objective of this review is to evaluate the emerging roles of SRT2104, and to explore its potential as a therapeutic agent in various diseases. In the present review, we systematically summarized the findings from an extensive array of literature sources including the progress of its application in disease treatment and its potential molecular mechanisms by reviewing the literature published in databases such as PubMed, Web of Science, and the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform. We focuses on the strides made in employing SRT2104 for disease treatment, elucidating its potential molecular underpinnings based on preclinical and clinical research data. The findings reveal that SRT2104, as a potent SIRT1 activator, holds considerable therapeutic potential, particularly in modulating metabolic and longevity-related pathways. This review establishes SRT2104 as a leading SIRT1 activator with significant therapeutic promise.
Keywords: Clinical trials; Disease treatment; Preclinical research; SIRT1; SRT2104.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sirt1 activator SRT2104 protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury via regulating microglia polarization by modulating Sirt1/NF-κB pathway.Brain Res. 2021 Feb 15;1753:147236. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147236. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33412146
-
P53/NRF2 mediates SIRT1's protective effect on diabetic nephropathy.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Aug;1866(8):1272-1281. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30959066
-
Axonal protection by a small molecule SIRT1 activator, SRT2104, with alteration of autophagy in TNF-induced optic nerve degeneration.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2020 May;64(3):298-303. doi: 10.1007/s10384-020-00731-6. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32157485
-
SIRT1/SREBPs-mediated regulation of lipid metabolism.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Jan;199:107037. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.107037. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 38070792 Review.
-
[Updated roles of SIRT1 in prostate diseases].Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2016 Apr;22(4):356-60. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2016. PMID: 30088710 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Sirtuins and Resveratrol in Cardiorenal Diseases: A Narrative Review of Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 30;17(7):1212. doi: 10.3390/nu17071212. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40218970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanochemical Approach for Metal-Free Regioselective C5-Sulfenylation of Imidazo[2,1-b]Thiazoles.ChemSusChem. 2025 Aug 6;18(16):e202500320. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202500320. Epub 2025 May 12. ChemSusChem. 2025. PMID: 40293326 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic kidney disease: exploring mechanistic depths and the future of pharmacological intervention.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug 19. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04534-9. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40828323 Review.
-
The SIRT1 activator SRT2104 exerts exercise mimetic effects and promotes Duchenne muscular dystrophy recovery.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Apr 7;16(1):259. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07595-z. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40195304 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Mitochondria Dysfunction in LMNA Cardiomyopathy.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2024 Oct 28;9(10):1231-1233. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2024.07.007. eCollection 2024 Oct. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39534634 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2020BSQD002/State Doctor Startup Fund of Shunde Women and Children's Hospital of Guangdong Medical University
- 2020BSQD003/State Doctor Startup Fund of Shunde Women and Children's Hospital of Guangdong Medical University
- 2021BSQD001/State Doctor Startup Fund of Shunde Women and Children's Hospital of Guangdong Medical University
- 2022A1515140167/GuangDong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

