Guiding the HBO1 complex function through the JADE subunit
- PMID: 38448574
- PMCID: PMC11320721
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01245-2
Guiding the HBO1 complex function through the JADE subunit
Abstract
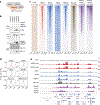
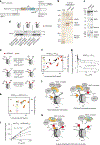
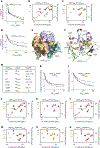
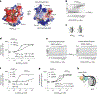
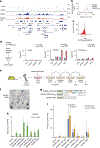
JADE is a core subunit of the HBO1 acetyltransferase complex that regulates developmental and epigenetic programs and promotes gene transcription. Here we describe the mechanism by which JADE facilitates recruitment of the HBO1 complex to chromatin and mediates its enzymatic activity. Structural, genomic and complex assembly in vivo studies show that the PZP (PHD1-zinc-knuckle-PHD2) domain of JADE engages the nucleosome through binding to histone H3 and DNA and is necessary for the association with chromatin targets. Recognition of unmethylated H3K4 by PZP directs enzymatic activity of the complex toward histone H4 acetylation, whereas H3K4 hypermethylation alters histone substrate selectivity. We demonstrate that PZP contributes to leukemogenesis, augmenting transforming activity of the NUP98-JADE2 fusion. Our findings highlight biological consequences and the impact of the intact JADE subunit on genomic recruitment, enzymatic function and pathological activity of the HBO1 complex.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
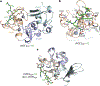
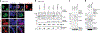
References
-
- Grunstein M Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature 389, 349–352 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Kuo MH & Allis CD Roles of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in gene regulation. Bioessays 20, 615–626 (1998). - PubMed
-
- MacPherson L et al. HBO1 is required for the maintenance of leukaemia stem cells. Nature 577, 266–270 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

