Integrated optical frequency division for microwave and mmWave generation
- PMID: 38448598
- PMCID: PMC10954543
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07057-0
Integrated optical frequency division for microwave and mmWave generation
Abstract
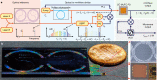
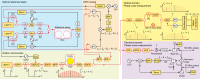
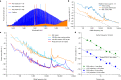
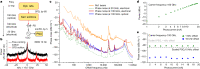
The generation of ultra-low-noise microwave and mmWave in miniaturized, chip-based platforms can transform communication, radar and sensing systems1-3. Optical frequency division that leverages optical references and optical frequency combs has emerged as a powerful technique to generate microwaves with superior spectral purity than any other approaches4-7. Here we demonstrate a miniaturized optical frequency division system that can potentially transfer the approach to a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor-compatible integrated photonic platform. Phase stability is provided by a large mode volume, planar-waveguide-based optical reference coil cavity8,9 and is divided down from optical to mmWave frequency by using soliton microcombs generated in a waveguide-coupled microresonator10-12. Besides achieving record-low phase noise for integrated photonic mmWave oscillators, these devices can be heterogeneously integrated with semiconductor lasers, amplifiers and photodiodes, holding the potential of large-volume, low-cost manufacturing for fundamental and mass-market applications13.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Koenig S, et al. Wireless sub-THz communication system with high data rate. Nat. Photonics. 2013;7:977–981. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.275. - DOI
-
- Long, D. & Ulaby, F. Microwave Radar and Radiometric Remote Sensing (Artech, 2015).
-
- Fortier TM, et al. Generation of ultrastable microwaves via optical frequency division. Nat. Photonics. 2011;5:425–429. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2011.121. - DOI
-
- Xie X, et al. Photonic microwave signals with zeptosecond-level absolute timing noise. Nat. Photonics. 2017;11:44–47. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2016.215. - DOI

