Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Advanced Systemic Mastocytosis: A retrospective analysis of the DRST and GREM registries
- PMID: 38448757
- PMCID: PMC10997505
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-024-02186-x
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Advanced Systemic Mastocytosis: A retrospective analysis of the DRST and GREM registries
Abstract
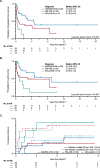
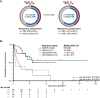
We identified 71 patients with AdvSM (aggressive SM [ASM], SM with an associated hematologic neoplasm [SM-AHN, e.g., acute myeloid leukemia, SM-AML], mast cell leukemia [MCL]) in two national registries (DRST/GREM) who received an allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT) performed in Germany from 1999-2021. Median overall survival (OS) of ASM/SM-AHN (n = 30, 45%), SM-AML (n = 28, 39%) and MCL ± AHN (n = 13, 19%) was 9.0, 3.3 and 0.9 years (P = 0.007). Improved median OS was associated with response of SM (17/41, 41%; HR 0.4 [0.2-0.9], P = 0.035) and/or of AHN (26/43, 60%, HR 0.3 [0.1-0.7], P = 0.004) prior to alloHCT. Adverse predictors for OS included absence of KIT D816V (10/61, 16%, HR 2.9 [1.2-6.5], P < 0.001) and a complex karyotype (9/60, 15%, HR 4.2 [1.8-10.0], P = 0.016). HLA-match, conditioning type or transplantation at centers reporting above-average alloHCTs (≥7) had no impact on OS. Taking into account competing events at years 1, 3 and 5, relapse-related mortality and non-relapse mortality rate were 15%/23%, 20%/30% and 23%/35%, respectively. Irrespective of subtype, subsequent treatment response was achieved in 13/30 (43%) patients and was highest on midostaurin/avapritinib (7/9, 78%). We conclude that outcome of alloHCT in AdvSM is more affected by disease phenotype and treatment response prior to transplant than by transplant characteristics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DC received consulting fees from Blueprint Medicines, Novartis, Pfizer and BeiGene, honoraria from Blueprint Medicines, Novartis and AstraZeneca and travel support from Amgen and Janssen. JS received consulting fees from Blueprint Medicines and GlaxoSmithKline, honoraria from Blueprint Medicines, GlaxoSmithKline and Novartis and research funding from GlaxoSmithKline. KS received consulting fees from Blueprint Medicines, honoraria from Astra Zeneca and Novartis and participated in the speakers bureau of BMS. MJ received consulting fees from Novartis and honoraria from Amgen, Blueprint Medicines, BMS, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis and Pfizer. KS received consulting fees and honoraria from Blueprint Medicines, BMS and Novartis, lecture fees from GlaxoSmithKline and research support from Active Biotech. IK received consulting fees from Novartis, honoraria from AbbVie, Medac, Novartis and Takeda and travel support from Medac, Amgen, BeiGene, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Janssen and Fondation Internationale Menarini. ES received consulting fees from Jazz Pharmaceuticals, BMS, Kite Gilead and Takeda, honoraria from Jazz Pharmaceuticals, BMS, Kite Gilead and Novartis and support for meeting attendance from Jazz Pharmaceuticals and Kite Gilead. SS received honoraria from Prothena, Janssen, Takeda and Pfizer, research funding from Prothena, Janssen and Sanofi and travel support from Prothena, Janssen, Celgene, Binding Site and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. MR received honoraria from BMS, Novartis, Takeda, Incyte, Corat, Cogent Biosciences, TEVA, Otsuka, Lilly, Abbvie, Pfizer, Beigene and GlaxoSmithKline, research funding from Novartis and travel support from BMS, Novartis, Abbvie, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Daiichi Sankyo, Amgen, Astellas, SOBI and AOP. THB received consulting fees from Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Novartis and Pfizer, honoraria from Janssen, Merck and Novartis, research funding from Novartis and Pfizer, participated in the speakers bureaus of Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Novartis and Pfizer and was paid for patents and royalties from Novartis. SK received honoraria from Amgen. EJ received honoraria from BMS, Jazz Pharmaceuticals and Amgen and travel support from Medac. AR received consulting fees, honoraria and research funding from Abbvie, AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals, Blueprint Medicines Corporation, BMS, GlaxoSmithKline, Incyte and Novartis and was member on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees of Abbvie, AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals, Blueprint Medicines, BMS, GSK, Incyte and Novartis. JP received consulting fees from Amgen, Apellis Pharmaceuticals, BMS, MSD and Sanofi and was member on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees and Speakers Bureau of Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease, Boehring Ingelheim, Blueprint Medicines, Novartis, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, SOBI and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

