Integrated analysis reveals FLI1 regulates the tumor immune microenvironment via its cell-type-specific expression and transcriptional regulation of distinct target genes of immune cells in breast cancer
- PMID: 38448802
- PMCID: PMC10916124
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10174-9
Integrated analysis reveals FLI1 regulates the tumor immune microenvironment via its cell-type-specific expression and transcriptional regulation of distinct target genes of immune cells in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Immunotherapy is a practical therapeutic approach in breast cancer (BRCA), and the role of FLI1 in immune regulation has gradually been unveiled. However, the specific role of FLI1 in BRCA was conflicted; thus, additional convincing evidence is needed.
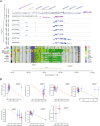
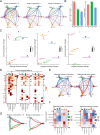
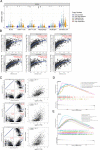
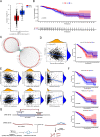
Methods: We explored the upstream regulation of FLI1 expression via summary data-based Mendelian randomization (SMR) analysis and ncRNA network construction centering on FLI1 using BRCA genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary data with expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) and DNA methylation quantitative trait loci (mQTLs) from the blood and a series of in silico analyses, respectively. We illuminated the downstream function of FLI1 in immune regulation by integrating a series of analyses of single-cell RNA sequence data (scRNA-seq).
Results: We verified a causal pathway from FLI1 methylation to FLI1 gene expression to BRCA onset and demonstrated that FLI1 was downregulated in BRCA. FLI1, a transcription factor, served as myeloid and T cells' communication regulator by targeting immune-related ligands and receptor transcription in BRCA tissues. We constructed a ceRNA network centering on FLI1 that consisted of three LncRNAs (CKMT2-AS1, PSMA3-AS1, and DIO3OS) and a miRNA (hsa-miR-324-5p), and the expression of FLI1 was positively related to a series of immune-related markers, including immune cell infiltration, biomarkers of immune cells, and immune checkpoints.
Conclusion: Low-methylation-induced or ncRNA-mediated downregulation of FLI1 is associated with poor prognosis, and FLI1 might regulate the tumor immune microenvironment via a cell-type-specific target genes manner in BRCA.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cell communication; FLI1; Immune cells; Transcription factor; scRNA-seq.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Watson DK, Smyth FE, Thompson DM, Cheng JQ, Testa JR, Papas TS, et al. The ERGB/Fli-1 gene: isolation and characterization of a new member of the family of human ETS transcription factors. Cell Growth Differ Mol Biol J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 1992;3:705–713. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

