Global epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in patients with NAFLD or MAFLD: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38448943
- PMCID: PMC10919055
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03315-0
Global epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in patients with NAFLD or MAFLD: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) shares common pathophysiological mechanisms with type 2 diabetes, making them significant risk factors for type 2 diabetes. The present study aimed to assess the epidemiological feature of type 2 diabetes in patients with NAFLD or MAFLD at global levels.
Methods: Published studies were searched for terms that included type 2 diabetes, and NAFLD or MAFLD using PubMed, EMBASE, MEDLINE, and Web of Science databases from their inception to December 2022. The pooled global and regional prevalence and incidence density of type 2 diabetes in patients with NAFLD or MAFLD were evaluated using random-effects meta-analysis. Potential sources of heterogeneity were investigated using stratified meta-analysis and meta-regression.
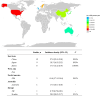
Results: A total of 395 studies (6,878,568 participants with NAFLD; 1,172,637 participants with MAFLD) from 40 countries or areas were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled prevalence of type 2 diabetes among NAFLD or MAFLD patients was 28.3% (95% confidence interval 25.2-31.6%) and 26.2% (23.9-28.6%) globally. The incidence density of type 2 diabetes in NAFLD or MAFLD patients was 24.6 per 1000-person year (20.7 to 29.2) and 26.9 per 1000-person year (7.3 to 44.4), respectively.
Conclusions: The present study describes the global prevalence and incidence of type 2 diabetes in patients with NAFLD or MAFLD. The study findings serve as a valuable resource to assess the global clinical and economic impact of type 2 diabetes in patients with NAFLD or MAFLD.
Keywords: Incidence density; Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Prevalence; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Hepatol. 2019 Oct;71(4):793-801. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021. Epub 2019 Jul 4. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31279902
-
Estimating Global Prevalence of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Overweight or Obese Adults.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Mar;20(3):e573-e582. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.02.030. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 33618024
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies on the potential association between NAFLD/MAFLD and risk of incident atrial fibrillation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 5;14:1160532. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1160532. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37476492 Free PMC article.
-
Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver and metabolic-associated fatty liver with COVID-19 outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jun 7;29(21):3362-3378. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i21.3362. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37377589 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease vs. type 2 diabetes mellitus non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a longitudinal cohort analysis.Ann Hepatol. 2023 Jan-Feb;28(1):100762. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2022.100762. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Ann Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36182031
Cited by
-
Diagnostic accuracy of Fatty Liver Index (FLI) for detecting Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in adults attending a tertiary care hospital, a cross-sectional study.Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024 Dec 13;10(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s40842-024-00197-2. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39668382 Free PMC article.
-
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Demonstrates Reliable Agreement with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry in Identifying Reduced Skeletal Muscle Mass in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Hypertension.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 16;14(20):2301. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14202301. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451624 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of High Adherence to Mediterranean Diet on the Risk of Incident Type-2 Diabetes in Subjects with MAFLD: The Di@bet.es Study.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 4;16(21):3788. doi: 10.3390/nu16213788. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519621 Free PMC article.
-
MASLD: Prevalence, Mechanisms, and Sex-Based Therapies in Postmenopausal Women.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 2;13(4):855. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13040855. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40299427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of type 2 diabetes on the risk of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular mortality in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a nationwide population-based study.BMJ Public Health. 2025 Jun 18;3(1):e002020. doi: 10.1136/bmjph-2024-002020. eCollection 2025. BMJ Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40548068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IDF diabetes Atlas. 9th edn. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation: International Diabetes Federation; 2019 Available from: https://www.diabetesatlas.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- M0294/345 Talent Project of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University
- 82003456/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82103811/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020QNRC001/Yong Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program by Cast
- CYJZ202102/Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital Golden Seeds Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

