Reorganization of 3D genome architecture provides insights into pathogenesis of early fatty liver disease in laying hens
- PMID: 38448979
- PMCID: PMC10919017
- DOI: 10.1186/s40104-024-01001-y
Reorganization of 3D genome architecture provides insights into pathogenesis of early fatty liver disease in laying hens
Abstract
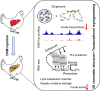
Background: Fatty liver disease causes huge economic losses in the poultry industry due to its high occurrence and lethality rate. Three-dimensional (3D) chromatin architecture takes part in disease processing by regulating transcriptional reprogramming. The study is carried out to investigate the alterations of hepatic 3D genome and H3K27ac profiling in early fatty liver (FLS) and reveal their effect on hepatic transcriptional reprogramming in laying hens.
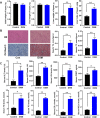
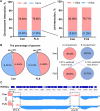
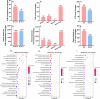
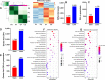
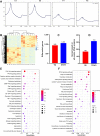
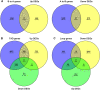
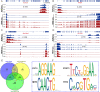
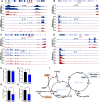
Results: Results show that FLS model is constructed with obvious phenotypes including hepatic visible lipid deposition as well as higher total triglyceride and cholesterol in serum. A/B compartment switching, topologically associating domain (TAD) and chromatin loop changes are identified by high-throughput/resolution chromosome conformation capture (HiC) technology. Targeted genes of these alternations in hepatic 3D genome organization significantly enrich pathways related to lipid metabolism and hepatic damage. H3K27ac differential peaks and differential expression genes (DEGs) identified through RNA-seq analysis are also enriched in these pathways. Notably, certain DEGs are found to correspond with changes in 3D chromatin structure and H3K27ac binding in their promoters. DNA motif analysis reveals that candidate transcription factors are implicated in regulating transcriptional reprogramming. Furthermore, disturbed folate metabolism is observed, as evidenced by lower folate levels and altered enzyme expression.
Conclusion: Our findings establish a link between transcriptional reprogramming changes and 3D chromatin structure variations during early FLS formation, which provides candidate transcription factors and folate as targets for FLS prevention or treatment.
Keywords: 3D chromatin architecture; Fatty liver disease; Folate; H3K27ac profiling; Transcription reprogramming.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

