A prognostic nomogram for predicting breast cancer survival based on mammography and AJCC staging
- PMID: 38449621
- PMCID: PMC10915383
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27072
A prognostic nomogram for predicting breast cancer survival based on mammography and AJCC staging
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: To develop a prognostic nomogram using mammography data and AJCC staging to predict breast cancer survival.
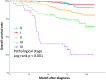
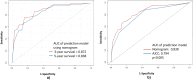
Materials and methods: A prognostic nomogram was created using data from 1000 women diagnosed with breast cancer at a medical cancer center in Taiwan between 2011 and 2015. The variables included age at diagnosis (≤60 or > 60 years), mammography purpose (screening or diagnostic), mammography modality (digital mammogram or digital breast tomosynthesis), and the 7th American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage. The outcome predicted was breast cancer-related mortality. The nomogram utilized Kaplan-Meier analysis for all subsets and Cox proportional hazards regression analysis for prediction. The nomogram's accuracy was internally validated using the concordance index and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, focusing on 3-year and 5-year survival predictions.
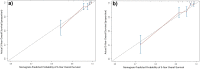
Results: Participants' mean age at breast cancer diagnosis was 54 years (SD = 11.2 years). The 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year overall survival (OS) rates were found to be 99.7%, 95.3%, and 91.4%, respectively. The bootstrap-corrected concordance indices indicated the following: nomogram, 0.807 and AJCC, 0.759. A significant difference was observed between the nomogram's area under the curve (AUC) and the AJCC stage in predicting the probability of 5-year survival (p = 0.005). A nomogram, constructed based on mammography and AJCC, demonstrated excellent calibration through internal validation using bootstrapping.
Conclusion: The utilization of a nomogram that incorporates mammography data and the AJCC registry data has been demonstrated to be a reliable predictor of breast cancer survival.
Keywords: AJCC staging; Breast cancer; Breast cancer survival; Mammography; Nomogram.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Duffy S.W., Tabar L., Yen A.M., Dean P.B., Smith R.A., Jonsson H., Tornberg S., Chen S.L., Chiu S.Y., Fann J.C., Ku M.M., Wu W.Y., Hsu C.Y., Chen Y.C., Svane G., Azavedo E., Grundstrom H., Sunden P., Leifland K., Frodis E., Ramos J., Epstein B., Akerlund A., Sundbom A., Bordas P., Wallin H., Starck L., Bjorkgren A., Carlson S., Fredriksson I., Ahlgren J., Ohman D., Holmberg L., Chen T.H. Mammography screening reduces rates of advanced and fatal breast cancers: results in 549,091 women. Cancer. 2020;126(13):2971–2979. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu S.G., Wang J., Lian C.L., Lei J., Hua L., Lin Q., Chen Y.X., He Z.Y. Evaluation of the 8th edition of the American joint committee on cancer's pathological staging system in prognosis assessment and treatment decision making for stage T1-2N1 breast cancer after mastectomy. Breast. 2020;51:2–10. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

