TREM1 promotes cancer associated malignant phenotype through activated MAPK signaling pathway and predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer
- PMID: 38449634
- PMCID: PMC10915522
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26852
TREM1 promotes cancer associated malignant phenotype through activated MAPK signaling pathway and predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: CD molecules plays a vital role in gastric cancer (GC). We used bioinformatics analysis methods to develop prognosis related CD molecules risk signature; On the other hand, we used the experiments to further explore the function and mechanism of differentially expressed prognostic CD molecules (TREM1) in GC.
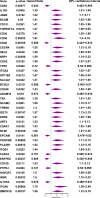
Methods: Kaplan-Meier survival and univariate Cox regression analysis were used to evaluate the overall survival of CD molecule genes in gastric cancer. ROC curve and Kaplan-Meier curves were used to analyze the predictive value of CD molecule related genes risk signature by "survival and timeROC" R packages. GSEA, and Cibersortx software were used to analyze the functional enrichment. Finally, we verified the function and mechanism of TREM1 in GC by gene silencing and MAPK inhibitor (SB203580) in vitro and vivo.
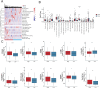
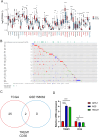
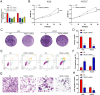
Results: A total of 41 prognosis related risk factors in gastric cancer were identified based on CD molecules, including TREM1 and ect. The high-risk patients had higher risk score and shorter survival time. ROC curves revealed that this risk signature accurately predicted survival times of gastric cancer patients at the 1-, 2-, 3-, 4- and 5-year. The frequency of T cells follicular helper and NK cells activated were added in low-risk group. Next, differentially expressed prognostic CD molecules analysis revealed that TREM1 was identified as key genes in GC progression based on TCGA and GES158662 and GSE15459 datasets of GC. In vitro experiments, TREM1 silencing significantly inhibited GC cell proliferation and migration, induced cell apoptosis. GSEA revealed that TREM1 activated cancer related signaling pathway, including MAPK signaling pathway and ect. High expression of TREM1 was related Macrophages M2 and Mast cells resting in GC tissues. Moreover, knockdown of TREM1 inhibited tumor growth through downregulated MAPK signaling pathway in vivo.
Conclusion: These results identified that CD molecule related genes as a novel prognostic and diagnostic biomarker in gastric cancer. TREM1 acts as an oncogene role in GC by activated MAPK signaling pathway.
Keywords: CD molecules; Gastric cancer; MAPK signaling pathway; Prognosis; TREM1.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIPPO signaling-related signature for predicting prognosis and therapeutic response in gastric cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 11;13:1096055. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1096055. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36712672 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of the prognostic value of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon (cGAS-STING) related genes in gastric cancer.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):1238-1250. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1911557. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 33843442 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cuproptosis-related subtypes, construction of a prognosis model, and tumor microenvironment landscape in gastric cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 21;13:1056932. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1056932. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36479114 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an EMT-Related Gene Signature for Predicting Overall Survival in Gastric Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 24;12:661306. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.661306. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34249086 Free PMC article.
-
TEAD4 functions as a prognostic biomarker and triggers EMT via PI3K/AKT pathway in bladder cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 May 17;41(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02377-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35581606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smyth E.C., et al. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2020;396(10251):635–648. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y., et al. The application of CA72-4 in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of gastric cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Canc. 2021;1876(2) - PubMed
-
- Sawaki K., Kanda M., Kodera Y. Review of recent efforts to discover biomarkers for early detection, monitoring, prognosis, and prediction of treatment responses of patients with gastric cancer. Expet Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018;12(7):657–670. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

