Immunization against inhibin DNA vaccine as an alternative therapeutic for improving follicle development and reproductive performance in beef cattle
- PMID: 38449672
- PMCID: PMC10916279
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1275022
Immunization against inhibin DNA vaccine as an alternative therapeutic for improving follicle development and reproductive performance in beef cattle
Abstract
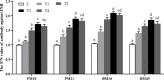
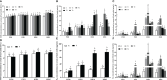
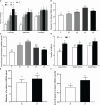
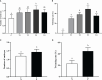
The objective of the present study was to investigate the potential role of immunization against INH on follicular development, serum reproductive hormone (FSH, E2, and P4) concentrations, and reproductive performance in beef cattle. A total of 196 non-lactating female beef cattle (4-5 years old) with identical calving records (3 records) were immunized with 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, or 2.0 mg [(T1, n = 58), (T2, n = 46), (T3, n = 42) and (T4, n = 36), respectively] of the pcISI plasmid. The control (C) group (n = 14) was immunized with 1.0 mL 0.9% saline. At 21d after primary immunization, all beef cattle were boosted with half of the primary immunization dose. On day 10 after primary immunization, the beef cattle immunized with INH DNA vaccine evidently induced anti-INH antibody except for the T1 group. The T3 group had the greatest P/N value peak among all the groups. The anti-INH antibody positive rates in T2, T3 and T4 groups were significantly higher than that in C and T1 groups. RIA results indicated that serum FSH concentration in T2 group increased markedly on day 45 after booster immunization; the E2 amount in T3 group was significantly increased on day 10 after primary immunization, and the levels of E2 also improved in T2 and T3 groups after booster immunization; the P4 concentration in T2 group was significantly improved on day 21 after primary immunization. Ultrasonography results revealed that the follicles with different diameter sizes were increased, meanwhile, the diameter and growth speed of ovulatory follicle were significantly increased. Furthermore, the rates of estrous, ovulation, conception, and twinning rate were also significantly enhanced. These findings clearly illustrated that INH DNA vaccine was capable of promoting the follicle development, thereby improving the behavioral of estrous and ovulation, eventually leading to an augment in the conception rates and twinning rate of beef cattle.
Keywords: beef cattle; immunization; inhibin; reproductive performance; vaccine.
Copyright © 2024 Meng, Li, Xiao, Liu, Gao, Gong, Lan and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nasal immunization with AMH-INH-RFRP DNA vaccine for improving follicle development and fertility in buffaloes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 20;14:1076404. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1076404. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36891049 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a DNA vaccine harboring two copies of inhibin α (1-32) fragments on immune response, hormone concentrations and reproductive performance in rats.Theriogenology. 2012 Jul 15;78(2):393-401. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2012.02.019. Epub 2012 May 15. Theriogenology. 2012. PMID: 22592078
-
Active immunization of heifers against a synthetic fragment of bovine inhibin.J Reprod Fertil. 1993 Jan;97(1):213-22. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0970213. J Reprod Fertil. 1993. PMID: 8464014
-
The effect of active immunization against inhibin on gonadotropin secretions and follicular dynamics during the estrous cycle in cows.J Reprod Dev. 2006 Feb;52(1):107-13. doi: 10.1262/jrd.17064. Epub 2005 Nov 18. J Reprod Dev. 2006. PMID: 16293939
-
Immunological manipulation of ovulation rate for twinning in cattle.J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1995;49:351-64. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1995. PMID: 7623326 Review.
Cited by
-
OCT angiography 2023 update: focus on diabetic retinopathy.Acta Diabetol. 2024 May;61(5):533-541. doi: 10.1007/s00592-024-02238-9. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Acta Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38376579 Review.
-
Combined Proteomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Comprehensive Regulation of Somatostatin DNA Vaccine in Goats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 23;25(13):6888. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136888. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roy F, Maurel MC, Combes B, Vaiman D, Cribiu EP, Lantier I, et al. . The negative effect of repeated equine chorionic gonadotropin treatment on subsequent fertility in Alpine goats is due to a humoral immune response involving the major histocompatibility complex. Biol Reprod (1999) 60:805–13. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod60.4.805 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

