Bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most cited studies in apolipoprotein E (ApoE) research
- PMID: 38449775
- PMCID: PMC10914050
- DOI: 10.52225/narraj.v1i1.2
Bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most cited studies in apolipoprotein E (ApoE) research
Abstract
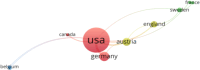
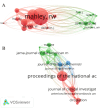
The apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is a glycoprotein which plays a vital role in different inflammatory conditions and in the catabolism of lipids and triglycerides. The aim of this study was to identify and evaluate the top 100 most cited studies on ApoE research. A bibliometric study was conducted. On January 18, 2021, studies published on ApoE were searched in the Web of Science Core Collection database without any limitations. The obtained data were analyzed for a number of attributes using HistCiteTM and VOSviewer software. The search yielded a total of 16,242 results. Of the total retrieved results, the top 100 most cited studies were selected. The top 100 most cited studies on ApoE were published from 1977 to 2017 and were cited 86,181 times. Single study citations ranged from 426 to 6,327. The studies were published in 41 journals authored by 589 authors. The study "Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families" was cited 6,327 times. Mahley RW, Roses AD, and Saunders AM were the most prolific authors who published ten studies each. Most of the studies were published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. A total of 151 institutions were involved, and the USA was the most productive country. Our finding provides valuable insight on ApoE research which may be useful for researchers, academia, and funding agencies to identify new future research domains.
Keywords: ApoE; Apolipoprotein E; VOSviewer; Web of Science; bibliometric analysis.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization Mapping of Anthrax Vaccine Publications from 1991 through 2021.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jun 23;10(7):1007. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10071007. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35891169 Free PMC article.
-
The top 100 most cited articles on mucopolysaccharidoses: a bibliometric analysis.Front Genet. 2024 Apr 12;15:1377743. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1377743. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38680422 Free PMC article.
-
The 100 Top-Cited Studies on Dyslexia Research: A Bibliometric Analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 22;12:714627. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.714627. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34366943 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most cited papers and research trends in breast cancer related BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 23;101(38):e30576. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030576. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36197199 Free PMC article.
-
Top 100 most-cited papers in core dental public health journals: bibliometric analysis.Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2021 Feb;49(1):40-46. doi: 10.1111/cdoe.12572. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2021. PMID: 32935344 Review.
Cited by
-
Trend of Polymer Research Related to COVID-19 Pandemic: Bibliometric Analysis.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Aug 12;14(16):3297. doi: 10.3390/polym14163297. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015553 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation mental training model: Mental Toughness Training Circle (MTTC).F1000Res. 2023 Feb 13;12:169. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.129010.1. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2023. PMID: 39262446 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric top ten healthcare-related ChatGPT publications in the first ChatGPT anniversary.Narra J. 2024 Aug;4(2):e917. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i2.917. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39280327 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 pandemic sheds a new research spotlight on antiviral potential of essential oils - A bibliometric study.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 29;9(7):e17703. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17703. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37456016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent update on cerebral sparganosis: A bibliometric analysis and scientific mapping.Narra J. 2024 Aug;4(2):e982. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i2.982. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39280299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marais AD. Apolipoprotein E in lipoprotein metabolism, health and cardiovascular disease. Pathology 2019;51(2):165-176. - PubMed
-
- Utermann G. Isolation and partial characterization of an Arginine-rich apolipoprotein from human plasma very-low-density lipoproteins: Apolipoprotein E. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem 1975;356(7):1113-1121. - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJet al. . Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science 1993;261(5123):921-923. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
