Prediction of risk factors for linezolid-induced thrombocytopenia based on neural network model
- PMID: 38449807
- PMCID: PMC10915059
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1292828
Prediction of risk factors for linezolid-induced thrombocytopenia based on neural network model
Abstract
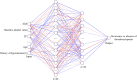
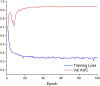
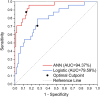
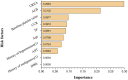
Background: Based on real-world medical data, the artificial neural network model was used to predict the risk factors of linezolid-induced thrombocytopenia to provide a reference for better clinical use of this drug and achieve the timely prevention of adverse reactions. Methods: The artificial neural network algorithm was used to construct the prediction model of the risk factors of linezolid-induced thrombocytopenia and further evaluate the effectiveness of the artificial neural network model compared with the traditional Logistic regression model. Results: A total of 1,837 patients receiving linezolid treatment in a hospital in Xi 'an, Shaanxi Province from 1 January 2011 to 1 January 2021 were recruited. According to the exclusion criteria, 1,273 cases that did not meet the requirements of the study were excluded. A total of 564 valid cases were included in the study, with 89 (15.78%) having thrombocytopenia. The prediction accuracy of the artificial neural network model was 96.32%, and the AUROC was 0.944, which was significantly higher than that of the Logistic regression model, which was 86.14%, and the AUROC was 0.796. In the artificial neural network model, urea, platelet baseline value and serum albumin were among the top three important risk factors. Conclusion: The predictive performance of the artificial neural network model is better than that of the traditional Logistic regression model, and it can well predict the risk factors of linezolid-induced thrombocytopenia.
Keywords: ADR; ANN; linezolid; logistic regression; risk factor; thrombocytopenia.
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Peng, Hu, Li, Ji, Dong, Huang, Piao, Ding and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Establishment of artificial neural network model for predicting lymph node metastasis in patients with stage Ⅱ-Ⅲ gastric cancer].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Apr 25;25(4):327-335. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441530-20220105-00010. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35461201 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Linezolid induced thrombocytopenia in critically ill patients: Risk factors and development of a machine learning-based prediction model.J Infect Chemother. 2022 Sep;28(9):1249-1254. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2022.05.004. Epub 2022 May 14. J Infect Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35581121
-
Establishment and validation of a risk prediction model incorporating concentrations of linezolid and its metabolite PNU142300 for linezolid-induced thrombocytopenia.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023 Aug 2;78(8):1974-1981. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkad191. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023. PMID: 37341139
-
Hematological toxicities associated with linezolid therapy in adults: key findings and clinical considerations.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Mar;16(3):219-230. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2023.2181160. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36787631 Review.
-
External Evaluation of Population Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Linezolid-Induced Thrombocytopenia: The Transferability of Published Models to Different Hospitalized Patients.Ther Drug Monit. 2021 Apr 1;43(2):271-278. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000816. Ther Drug Monit. 2021. PMID: 33009290
Cited by
-
Risk Stratification for Cephalosporin-Induced Thrombocytopenia: Development and Validation of a Multidimensional Predictive Model in Older Adults.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025 Jun 25;18:2107-2120. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S529488. eCollection 2025. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025. PMID: 40589539 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram incorporating linezolid and metabolite concentrations for predicting linezolid induced thrombocytopenia in patients with renal impairment.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 30;14(1):26064. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77768-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39478050 Free PMC article.
-
High accumulation of linezolid and its major metabolite in the serum of patients with hepatic and renal dysfunction is significantly associated with thrombocytopenia and anemia.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jul;13(7):e0249324. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02493-24. Epub 2025 May 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40387405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An R. F., Wang L. L. (2013). Linezolid-induced thrombocytopenia. Chin. J. New Drugs 22 (12), 1469–1472.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

