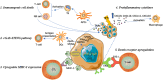
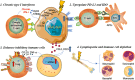
Immune modulatory roles of radioimmunotherapy: biological principles and clinical prospects
- PMID: 38449871
- PMCID: PMC10915027
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1357101
Immune modulatory roles of radioimmunotherapy: biological principles and clinical prospects
Abstract
Radiation therapy (RT) not only can directly kill tumor cells by causing DNA double-strand break, but also exerts anti-tumor effects through modulating local and systemic immune responses. The immunomodulatory effects of RT are generally considered as a double-edged sword. On the one hand, RT effectively enhances the immunogenicity of tumor cells, triggers type I interferon response, induces immunogenic cell death to activate immune cell function, increases the release of proinflammatory factors, and reshapes the tumor immune microenvironment, thereby positively promoting anti-tumor immune responses. On the other hand, RT stimulates tumor cells to express immunosuppressive cytokines, upregulates the function of inhibitory immune cells, leads to lymphocytopenia and depletion of immune effector cells, and thus negatively suppresses immune responses. Nonetheless, it is notable that RT has promising abscopal effects and may achieve potent synergistic effects, especially when combined with immunotherapy in the daily clinical practice. This systematic review will provide a comprehensive profile of the latest research progress with respect to the immunomodulatory effects of RT, as well as the abscopal effect of radioimmunotherapy combinations, from the perspective of biological basis and clinical practice.
Keywords: abscopal effect; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immune modulation; radiotherapy; review.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Wang, Zhang, Shi, Liu, Wang, Wang, Chen, Shi and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oncolytic reovirus enhances the effect of CEA immunotherapy when combined with PD1-PDL1 inhibitor in a colorectal cancer model.Immunotherapy. 2025 Apr;17(6):425-435. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2501926. Epub 2025 May 12. Immunotherapy. 2025. PMID: 40353308
-
Low-dose radiotherapy enhances the efficacy of PD-L1 blockade and induces the abscopal effect.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Jun 30;13(6):e011487. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2025-011487. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40588370 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
Cited by
-
The Role of Immunotherapy and Immune Modulators in Hormone-Positive Breast Cancer: Implications for Localized and Metastatic Disease.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 17;14(12):4322. doi: 10.3390/jcm14124322. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40566067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic nanovaccines in cancer therapy: mechanisms, efficacy, and clinical translation.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 18;34:102116. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102116. eCollection 2025 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40791791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 inhibitor AZ1 alone and in combination with cisplatin for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Apoptosis. 2024 Oct;29(9-10):1793-1809. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-02008-6. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 39222275 Free PMC article.
-
Propensity score analysis of high-dose rate brachytherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and docetaxel in second-line advanced NSCLC treatment.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 12;15(1):12650. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97918-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40221605 Free PMC article.
-
From cold to hot: mechanisms of hyperthermia in modulating tumor immunology for enhanced immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 28;16:1487296. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1487296. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40092992 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources