Bibliometric Analysis of Research Papers on Academic Stress (1989-2023)
- PMID: 38449911
- PMCID: PMC10915691
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.55536
Bibliometric Analysis of Research Papers on Academic Stress (1989-2023)
Abstract
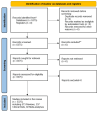
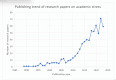
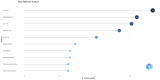
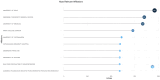
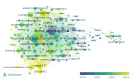
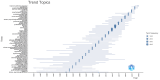
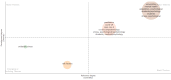
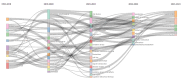
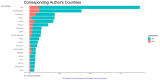
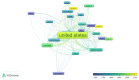
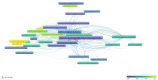
This extensive study provides a comprehensive overview of the contemporary research landscape about academic stress, emphasizing on identifying the most relevant contributors and understanding prevalent trends. The analysis included 5,375 results from the PubMed database and revealed a consistent upward trajectory with fluctuations in research paper publications over the years. Network analysis and visualization were performed using the Biblioshiny app and VOSviewer software. The analysis identified that the University of Oslo has published the highest number of research papers related to academic stress. In contrast, the Netherlands, the USA, and Australia demonstrated the highest frequency of collaboration. Analysis of keywords and their co-occurrence provides an overview of the research focus and the areas associated with psychological stress due to academics. Thematic evaluation and topic trend analysis provided insights into the evolving nature of research in academic stress. The thematic map depicts two categories of themes - motor themes, including psychological stress, its epidemiology, the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the mental health of university students, particularly those in medical programs; and emerging themes, including oxidative stress and risk factors, indicated evolving areas of interest. A notable observation was the scarcity of research on primary school students, signaling a gap in the existing academic stress literature. Citation analysis identified the most cited authors, countries, universities, and sources. This multifaceted examination provides a nuanced understanding of academic stress research's current state and dynamics, offering valuable insights into trends, collaborations, and thematic shifts that will guide future research in this critical field.
Keywords: academic stress; bibliometric; citation analysis; mental health; network analysis; network visualisation; overlay visualisation; psychological stress; stress; thematic analysis.
Copyright © 2024, Dagli et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Navigating the Web of Influence: A Bibliometric Analysis of Social Media Addiction.Cureus. 2024 Jun 13;16(6):e62283. doi: 10.7759/cureus.62283. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39006596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the Evolution of Clinical Trials on Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: A Bibliometric Overview (1965-2023).Cureus. 2024 Feb 28;16(2):e55190. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55190. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38425326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric study of immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1210802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1210802. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and repercussions of stress and mental health issues on primary and middle school students: a bibliometric analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 9;15:1369605. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1369605. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39315327 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of global research in palliative care for cervical cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 26;14:1432805. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1432805. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39252942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stress, mental symptoms and well-being in students: a gender analysis.Front Psychol. 2024 Dec 11;15:1492324. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1492324. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39742046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Is the OSCE more stressful? Examination anxiety and its consequences in different assessment methods in dental education. Brand HS, Schoonheim-Klein M. Eur J Dent Educ. 2009;13:147–153. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
