Bilateral Blunt Traumatic Dissections of the Extracranial Internal Carotid Artery: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 38449976
- PMCID: PMC10917072
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.53630
Bilateral Blunt Traumatic Dissections of the Extracranial Internal Carotid Artery: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
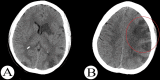
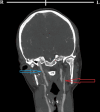
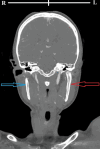
Bilateral traumatic dissections of the cervical internal carotid artery (ICA) are rare complications of polytrauma. A thorough literature review was performed, and data from selected studies were analyzed to assess the trends in clinical presentation, modes of trauma, management protocols, and clinical outcomes. The reported outcomes were categorized and graded into optimal, intermediate, and poor outcomes. We describe a rare case of bilateral dissection of ICA in a 31-year-old woman who was involved in a motor vehicle accident. She had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 9 and right-sided hemiparesis. Radiological findings revealed left upper ICA dissection, arterial intramural thrombus, and stenosis of the upper segment of the right ICA. She improved on conservative management and had a good clinical outcome at a three-month follow-up. Emergency physicians must be knowledgeable about such cases, as more than half of these trauma victims are initially asymptomatic on initial presentation. Specific diagnostic and therapeutic modalities should be implemented based on low threshold clinical suspicion to avoid missing these potentially disabling injuries and reduce morbidity and mortality. Computed tomographic angiography is recommended in cases with atypical clinical presentations, unexplained neurological deficits, or delayed-onset clinical deterioration. While antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapies are the mainstays of conservative management, endovascular and surgical management are only used in severe cases when medical treatment has failed, the artery has been completely transected, or there is active bleeding. Generally, good outcomes were reported in about two-thirds of those patients.
Keywords: cervical; dissections; internal carotid artery; traumatic brain injury; vascular dissection.
Copyright © 2024, Khormi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Traumatic dissection of the carotid artery: challenges for diagnostics and therapy illustrated by a case example (Article in German) Jansen G, Popp J, Dietrich U, Mertzlufft F, Bach F. Anaesthesist. 2013;62:817–823. - PubMed
-
- What are the expected findings on follow-up computed tomography angiogram in post-traumatic patients with blunt cerebrovascular Injury? Elbanna KY, Mohammed MF, Choi JI, et al. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2018;69:266–276. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
