New insights into the role of the oral leukoplakia microenvironment in malignant transformation
- PMID: 38450102
- PMCID: PMC10914962
- DOI: 10.3389/froh.2024.1363052
New insights into the role of the oral leukoplakia microenvironment in malignant transformation
Abstract
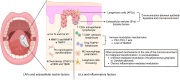
Oral leukoplakia is the most frequent and potentially malignant lesion of the oral cavity. Although dysplasia grading remains the main factor for risk assessment, challenges persist in determining the exact risk of transformation, and the literature has focused on studying alternative biomarkers. The interaction between dysplastic epithelial cells and the microenvironment starts early, and the communication is mainly mediated by lymphocytes, inflammatory factors, fibroblasts, and the extracellular matrix, leading to dysplastic progression. Leukoplakia-infiltrating leukocytes (LILs) and leukoplakia-associated fibroblasts (LAFs) play crucial roles in the dysplastic microenvironment. The immune response is related to intraepithelial T lymphocyte infiltration, mechanisms of immunosuppression coordinated by regulatory T cells, M2 macrophage polarization, and increased numbers of Langerhans cells; in contrast, fibroblastic and extracellular matrix factors are associated with increased numbers of pro-tumorigenic myofibroblasts, increased expression of metalloproteinases vs. decreased expression of TIMPs, and increased expression of chemokines and other inflammatory mediators. The microenvironment offers insights into the progression of leukoplakia to carcinoma, and understanding the complexity of the oral microenvironment in potentially malignant diseases aids in determining the risk of malignant transformation and proposing new therapeutic alternatives.
Keywords: dysplasia; fibroblast; lymphocyte; malignant transformation; microenvironment; oral cancer; oral leukoplakia; premalignant.
© 2024 González-Arriagada, Canedo-Marroquín, Adorno-Farías and Fernández-Ramires.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declared that they were editorial board members of Frontiers at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

