Unraveling the dynamics of wheat leaf blight complex: isolation, characterization, and insights into pathogen population under Indian conditions
- PMID: 38450160
- PMCID: PMC10915091
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1287721
Unraveling the dynamics of wheat leaf blight complex: isolation, characterization, and insights into pathogen population under Indian conditions
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Unraveling the dynamics of wheat leaf blight complex: isolation, characterization, and insights into pathogen population under Indian conditions.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 12;15:1409209. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1409209. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38680923 Free PMC article.
Abstract
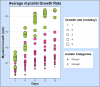
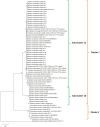
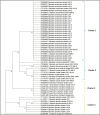
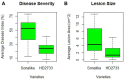
Wheat, a staple food crop for 35% of the global population, faces a threat from Helminthosporium leaf blight (HLB), a complex of spot blotch (Bipolaris sorokiniana) and tan spot (Pyrenophora-tritici-repentis) diseases under warm and humid conditions. However, in Indian conditions, the knowledge of existing pathogen populations associated with the HLB complex is limited and largely dominated by only B. sorokiniana (spot blotch). To address this, diseased samples were collected from all six wheat growing zones during 2020-2022. The pathogenic species were identified through in-depth morphological characterization, supplemented with ITS-rDNA and GAPDH sequence analysis, a diagnostic SCAR marker, and pathogenicity studies on two wheat varieties: Sonalika and HD2733. The 32 isolates collected from 10 different states consist of B. spicifera (12.5% of all isolates), Exserohilum rostratum (9.3%), Bipolaris oryzae (3.1%), and B. sorokiniana (75%). B. sorokiniana exhibited the highest disease severity on both varieties. Other lesser-known pathogenic species also produced comparable disease severity as B. sorokiniana isolates and, therefore are economically important. Unraveling pathogen composition and biology aids in disease control and resistance breeding. Our study highlights economically impactful and lesser-known pathogenic species causing wheat leaf blight/spot blotch in India, guiding both current management and future resistance breeding strategies in plant pathology.
Keywords: Bipolaris spicifera; Exserohilum rostratum; absolute quantification; leaf blight/spot blotch complex; soil population dynamics; wheat.
Copyright © 2024 Aditya, Aggarwal, Bashyal, Gurjar, Saharan and Aggarwal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Survey, isolation and characterisation of Bipolaris sorokiniana (Shoem.) causing spot blotch disease in wheat under the climatic conditions of the Indo-Gangetic plains of India.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 14;10(22):e40398. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40398. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39624279 Free PMC article.
-
Corrigendum: Unraveling the dynamics of wheat leaf blight complex: isolation, characterization, and insights into pathogen population under Indian conditions.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 12;15:1409209. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1409209. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38680923 Free PMC article.
-
A New ToxA Haplotype in the Wheat Fungal Pathogen Bipolaris sorokiniana.Phytopathology. 2024 Jul;114(7):1525-1532. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-10-23-0370-R. Epub 2024 Jun 29. Phytopathology. 2024. PMID: 38530294
-
Genetics and breeding for resistance against four leaf spot diseases in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 29;14:1023824. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1023824. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37063191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bipolaris sorokiniana-Induced Black Point, Common Root Rot, and Spot Blotch Diseases of Wheat: A Review.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Mar 11;11:584899. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.584899. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33777829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Survey, isolation and characterisation of Bipolaris sorokiniana (Shoem.) causing spot blotch disease in wheat under the climatic conditions of the Indo-Gangetic plains of India.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 14;10(22):e40398. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40398. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39624279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya K., Dutta A. K., Pradhan P. (2011). “Bipolaris sorokiniana” (Sacc.) Shoem.: the most destructive wheat fungal pathogen in the warmer areas. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 5, 1064–1071. doi: 10.3316/informit.044224283000719 - DOI
-
- Adlakha K. L., Wilcoxson R. D., Raychaudhuri S. P. (1984). Resistance of wheat to leaf spot caused by Bipolaris sorokiniana [resistant cultivars, India]. Plant Dis. 68:320. doi: 10.1094/PD-68-320 - DOI
-
- Aggarwal R., Agarwal S., Sharma S., Gurjar M. S., Bashyal B. M., Rao A. R. (2021). Whole-genome sequence analysis of Bipolaris sorokiniana infecting wheat in India and characterization of ToxA gene in different isolates as pathogenicity determinants. 3 Biotech 12:151. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03213-3, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal R., Agrawal S., Gurjar M. S., Bashyal B. M., Saharan M. S. (2022). “Biology and management of spot blotch pathogen Bipolaris sorokiniana of wheat” in Fungal diversity, ecology and control management. eds. Rajpal V. R., Singh I., Navi S. S. (Singapore: Springer Nature; ), 3–26.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

