Case report: BCR-ABL-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia with bone destruction: a treatment dilemma
- PMID: 38450181
- PMCID: PMC10915032
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1356311
Case report: BCR-ABL-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia with bone destruction: a treatment dilemma
Abstract
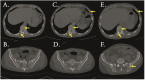
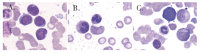
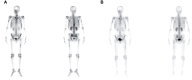
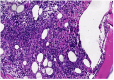
Although bone destruction and hypercalcemia without acute peripheral blast BCR-ABL-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) have been reported in children, they are rare in adults. Herein, we describe a case of BCR-ABL positive ALL with a triploid karyotype, WT1, and CDKN2A mutations with hypercalcemia and bone destruction as the first manifestations. Complete remission (CR) was achieved by induction chemotherapy. BCR-ABL turned negative after treatment with dasatinib. However, computed tomography and whole-body bone scan showed extensive bone destruction. Additionally, bone biopsy showed leukemic infiltration. After treatment with dasatinib and VMCP, leukemia recurred with positive BCR-ABL. The T315I mutation occurred. The patient was surgically diagnosed with calculous cholecystitis and achieved CR2 by postoperative orebatinib and VP regimens. Later, the patient died due to a severe pulmonary infection. BCR-ABL-positive ALL with bone destruction is rare and difficult to control using tyrosine kinase inhibitor chemotherapy alone. Therefore, further exploration of more effective treatments is needed.
Keywords: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; hypercalcemia; osteolysis; osteolytic bone lesions; protein kinase inhibitors.
Copyright © 2024 Lijun, Zhongrui, Li, Xia, Wei and Yaning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dasatinib: a tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia and philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Clin Ther. 2007 Nov;29(11):2289-308. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.11.005. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18158072 Review.
-
Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients already harbor BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations at low levels at the time of diagnosis.Haematologica. 2011 Apr;96(4):552-7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.034173. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Haematologica. 2011. PMID: 21193419 Free PMC article.
-
Drug resistance and BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia from the imatinib to the second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor era: The main changes are in the type of mutations, but not in the frequency of mutation involvement.Cancer. 2014 Apr 1;120(7):1002-9. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28522. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24382642
-
Treatment of human pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Aurora kinase inhibitor PHA-739358 (Danusertib).Mol Cancer. 2012 Jun 21;11:42. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-42. Mol Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22721004 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cancer. 2007 Sep 15;110(6):1178-86. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22881. Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17701954 Review.
References
-
- Virijević M, Vidović A, Colović N, Djunić I, Mitrović M, Suvajdić-Vuković N, et al. . Hypercalcemia with multiple osteolytic lesions and increased circulating tumor necrosis factor in an adult patient with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Srp Arh Celok Lek (2016) 144:207–10. doi: 10.2298/SARH1604207V. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shimonodan H, Nagayama J, Nagatoshi Y, Hatanaka M, Takada A, Iguchi H, et al. . Acute lymphocytic leukemia in adolescence with multiple osteolytic lesions and hypercalcemia mediated by lymphoblast-producing parathyroid hormone-related peptide: a case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Blood Cancer (2005) 45:333–9. doi: 10.1002/pbc.20357. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

