Comprehensive landscape and future perspectives of non-coding RNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, a bibliometric analysis from 2008 to 2023
- PMID: 38450329
- PMCID: PMC10915033
- DOI: 10.3389/pore.2024.1611595
Comprehensive landscape and future perspectives of non-coding RNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, a bibliometric analysis from 2008 to 2023
Abstract
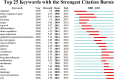
Objectives: Summarize the progress and hot topic evolution of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) research in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) in recent years and predict future research directions. Methods: Relevant articles from the Web of Science until 31 October 2023 were obtained. Bibliometric analysis of included articles was performed using software (VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and Bibliometrix). The volume and citation of publications, as well as the country, institution, author, journal, keywords of the articles were used as variables to analyze the research trends and hot spot evolution. Results: 1,118 literature from 2008 to 2023 were retrieved from database, with 25 countries/regions, 793 institutions, 5,426 authors, 261 journals involved. Global cooperation was centered on China, Japan, and the United States. Zhengzhou University, an institution from China, had the highest publication. The most prolific author was Guo Wei, and the most prolific journal was Oncology Letters. Analysis of keywords revealed that the research in this field revolved around the role of ncRNAs in the occurrence, development, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of ESCC, mainly including micro RNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and then circular RNAs. Conclusion: Overall, research on ncRNAs in ESCC remains strong. Previous research has mainly focused on the basic research, with a focus on the mechanism of ncRNAs in the occurrence, development, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of ESCC. Combining current research with emerging disciplines to further explore its mechanisms of action or shifting the focus of research from preclinical research to clinical research based on diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis, will be the main breakthrough in this field in the future.
Keywords: VOSviewer; bibliometric analysis; digestive system cancer; non-coding RNAs; novel biomarker.
Copyright © 2024 Wu, Wang, Cheng, Cheng and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

