Functional Laryngectomy and Quality of Life in Survivors of Head and Neck Cancer With Intractable Aspiration
- PMID: 38451502
- PMCID: PMC10921343
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoto.2024.0049
Functional Laryngectomy and Quality of Life in Survivors of Head and Neck Cancer With Intractable Aspiration
Abstract
Importance: Late effects of head and neck cancer (HNC) treatment include profound dysphagia, chronic aspiration, and death. Functional laryngectomy (FL) can improve patient survival and quality of life (QoL); however, removing a failing larynx for a noncancer reason is a difficult decision. Data regarding the ability of FL to improve self-perceptions of voice, swallowing, and QOL in survivors of HNC with intractable aspiration are inconclusive.
Objective: To investigate the association of FL with changes in self-reported perceptions of voice, swallowing, oral intake, QoL, and mood in survivors of HNC experiencing profound dysphagia and intractable aspiration.
Design, settings, and participants: This cohort study was conducted at a single academic institution and included survivors of HNC with profound swallowing dysfunction and intractable aspiration who underwent FL from July 2016 through March 2022. Of the initial 22 patients enrolled, 2 patients (15%) died of aspiration pneumonia before receiving FL. Data analyses were performed from July 2016 through March 2023.
Main outcomes and measures: Self-reported measures of voice using the VHI (30-item Voice Handicap Index), swallowing using the EAT-10 (10-item Eating Assessment Tool), functional oral intake scale using the FOIS (Functional Oral Intake Scale), and quality of life using the FACT-H&N (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Head & Neck) were assessed before FL and at 1, 3, and 6 months after FL. Mood states were evaluated using the POMS (Profile of Mood States, second edition), before FL and at 6 months after FL.
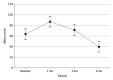
Results: The study analyses included 20 patients (mean [SD] age, 72.4 (7.0) years; 19 [95%] males and 1 [5%] female) who underwent FL and had complete data across all time points. Among these, 12 patients (60%) had received chemoradiation for oropharyngeal, 7 (35%) for laryngeal, or 1 (5%) for nasopharyngeal cancer. The mean (SD) time from completion of oncologic treatment to FL was 15.5 (5.5) years. Mean (SD) score on the EAT-10 improved from 33.2 (7.4) to 23.1 (10.8) at 1 month; 12.1 (9.1) at 3 months; and 8.3 (7.4) at 6 months, with a large effect size (η2 = 0.72; 95% CI, 0.54-0.80). Mean (SD) score on the FOIS improved from 2.0 (1.5) to 2.9 (1.7) at 1 month; 4.8 (2.5) at 3 months; and 5.2 (1.7) at 6 months, with a large effect size (η2 = 0.6; 95% CI, 0.38-0.71). Improvement in oral intake was achieved in 19 patients (95%), and feeding tubes were removed in 10 of 16 patients (63%) who were feeding tube-dependent; 6 patients (27%) continued to require supplemental tube feedings. Mean (SD) score on the VHI improved from 63.6 (34.0) to 86.9 (33.7) at 1 month; 71.3 (36.1) at 3 months; and 39.7 (26.9) at 6 months, with a large effect size (η2 = 0.42; 95% CI, 0.19-0.56). Seventeen patients (85%) were able to use a tracheoesophageal voice prosthesis for alaryngeal communication. Mean (SD) score on the FACT-H&N improved from 86.2 (17.8) to 93.6 (18.4) at 1 month; 109.0 (18.4) at 3 months; and 121.0 (16.8) at 6 months, with a large effect size (η2 = 0.64; 95% CI, 0.42-0.74). Mean (SD) score on the POMS improved from 58.9 (13.2) at baseline to 44.5 (9.9) at 6 months, with a large effect size (Cohen d = 1.04; 95% CI, 0.48-1.57). None of the patients experienced major complications of FL; 1 patient (5%) had a postoperative pharyngocutaneous fistula.
Conclusions and relevance: The findings of this cohort study indicate that FL was associated with marked improvements in self-perception of voice and swallowing, functional oral intake, QoL, and mood state among survivors of HNC. These findings can serve as a framework for FL counseling among HNC survivors experiencing profound dysphagia and intractable aspiration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Safety and efficacy of functional laryngectomy for end-stage dysphagia.Laryngoscope. 2018 Mar;128(3):597-602. doi: 10.1002/lary.26760. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Laryngoscope. 2018. PMID: 28714539
-
Prospective clinical study on long-term swallowing function and voice quality in advanced head and neck cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy and preventive swallowing exercises.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Nov;272(11):3521-31. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3379-6. Epub 2014 Nov 8. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 25381096 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Pretreatment Dysphagia on Postchemoradiation Swallowing Function in Head and Neck Cancer.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Mar;166(3):506-510. doi: 10.1177/01945998211009853. Epub 2021 May 4. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 33940987
-
Nutrition impact symptoms and associated outcomes in post-chemoradiotherapy head and neck cancer survivors: a systematic review.J Cancer Surviv. 2018 Aug;12(4):479-494. doi: 10.1007/s11764-018-0687-7. Epub 2018 Mar 20. J Cancer Surviv. 2018. PMID: 29556926
-
Dysphagia following chemoradiation for locally advanced head and neck cancer.Ann Oncol. 2004 Mar;15(3):383-8. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdh101. Ann Oncol. 2004. PMID: 14998839 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of ondansetron orally soluble pellicle for preventing moderate- to high-emetic risk chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jan 6;25(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13406-z. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39762809 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

