Influence of nutritional supplements on antibody levels in pregnant women vaccinated with inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
- PMID: 38452000
- PMCID: PMC10919710
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289255
Influence of nutritional supplements on antibody levels in pregnant women vaccinated with inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
Abstract
Background: Because of the significantly higher demand for nutrients during pregnancy, pregnant women are more likely to have nutrient deficiencies, which may adversely affect maternal and fetal health. The influence of nutritional supplements on the immune effects of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines during pregnancy is not clear.
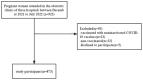
Methods: In a multicenter cross-sectional study, we enrolled 873 pregnant women aged 18-45 y in Guangdong, China. The general demographic characteristics of pregnant women and their use of nutritional supplements were investigated, and the serum antibody levels induced by inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines were measured. A logistic regression model was used to analyze the association between nutritional supplements and SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels.
Results: Of the 873 pregnant women enrolled, 825 (94.5%) took folic acid during pregnancy, 165 (18.9%) took iron supplements, and 197 (22.6%) took DHA. All pregnant women received at least one dose of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, and the positive rates of serum SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies were 44.7% and 46.4%, respectively. After adjustment for confounding factors, whether pregnant women took folic acid, iron supplements, or DHA did not influence NAb positivity or IgG positivity (P > 0.05). Compared with pregnant women who did not take folic acid, the odds ratios (ORs) for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 NAb and IgG antibody in pregnant women who took folic acid were 0.67 (P = 0.255; 95% CI, 0.34-1.32) and 1.24 (P = 0.547; 95% CI, 0.60-2.55), respectively. Compared with pregnant women who did not take iron supplements, the ORs for the presence of NAb and IgG antibody in pregnant women who took iron supplements were 1.16(P = 0.465; 95% CI, 0.77-1.76) and 0.98 (P = 0.931; 95% CI, 0.64-1.49), respectively. Similarly, the ORs for NAb and IgG antibody were 0.71 (P = 0.085; 95% CI, 0.49-1.04) and 0.95 (P = 0.801; 95% CI, 0.65-1.38) in pregnant women who took DHA compared with those who did not.
Conclusions: Nutritional supplementation with folic acid, iron, or DHA during pregnancy was not associated with antibody levels in pregnant women who received inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines.
Copyright: © 2024 Zhang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Similar articles
-
Immune response and safety of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines during pregnancy: a real-world observational study.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2023 Jan-Dec;22(1):956-963. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2023.2272655. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2023. PMID: 37855091
-
Long-Term Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies and Impact of Inactivated Vaccine on SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Based on a COVID-19 Patients Cohort.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 27;13:829665. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.829665. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35154152 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses Induced by Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccines in a Real-World Setting.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:802858. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.802858. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003131 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal nutrients and effects of gestational COVID-19 infection on fetal brain development.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021 Jun;43:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.04.019. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021. PMID: 34024500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactoferrin Supplementation in Preventing and Protecting from SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Is There Any Role in General and Special Populations? An Updated Review of Literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 24;25(19):10248. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910248. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408576 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of folic acid supplementation before conception on innate immunity and anti-HBs levels of offspring born to HBsAg-positive mothers.Front Nutr. 2025 Apr 23;12:1526053. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1526053. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40336960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skirrow H, Barnett S, Bell S, Riaposova L, Mounier-Jack S, Kampmann B, et al.. Women’s views on accepting COVID-19 vaccination during and after pregnancy, and for their babies: a multi-methods study in the UK. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. (2022) Jan 14;22(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12884-021-04321-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Luxi N, Giovanazzi A, Capuano A, Crisafulli S, Cutroneo PM, Fantini MP, et al.. COVID-19 Vaccination in Pregnancy, Paediatrics, Immunocompromised Patients, and Persons with History of Allergy or Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Overview of Current Recommendations and Pre- and Post-Marketing Evidence for Vaccine Efficacy and Safety. Drug Saf. (2021) Dec;44(12):1247–1269. doi: 10.1007/s40264-021-01131-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous