Temporal trends of severity and outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 after the emergence of variants of concern: A comparison of two waves
- PMID: 38452031
- PMCID: PMC10919739
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299607
Temporal trends of severity and outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 after the emergence of variants of concern: A comparison of two waves
Abstract
Background: The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants led to subsequent waves of COVID-19 worldwide. In many countries, the second wave of COVID-19 was marked by record deaths, raising the concern that variants associated with that wave might be more deadly. Our aim was to compare outcomes of critically-ill patients of the first two waves of COVID-19.
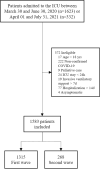
Methods: This retrospective cohort included critically-ill patients admitted between March-June 2020 and April-July 2021 in the largest academic hospital in Brazil, which has free-access universal health care system. We compared admission characteristics and hospital outcomes. The main outcome was 60-day survival and we built multivariable Cox model based on a conceptual causal diagram in the format of directed acyclic graph (DAG).
Results: We included 1583 patients (1315 in the first and 268 in the second wave). Patients in the second wave were younger, had lower severity scores, used prone and non-invasive ventilatory support more often, and fewer patients required mechanical ventilation (70% vs 80%, p<0.001), vasopressors (60 vs 74%, p<0.001), and dialysis (22% vs 37%, p<0.001). Survival was higher in the second wave (HR 0.61, 95%CI 0.50-0.76). In the multivariable model, admission during the second wave, adjusted for age, SAPS3 and vaccination, was not associated with survival (aHR 0.85, 95%CI 0.65-1.12).
Conclusions: In this cohort study, patients with COVID-19 admitted to the ICU in the second wave were younger and had better prognostic scores. Adjusted survival was similar in the two waves, contrasting with record number of hospitalizations, daily deaths and health system collapse seen across the country in the second wave. Our findings suggest that the combination of the burden of severe cases and factors such as resource allocation and health disparities may have had an impact in the excess mortality found in many countries in the second wave.
Copyright: © 2024 Freitas et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Ferreira reports personal fees from Medtronic, outside the submitted work; Dr. Costa reports personal fees from Timpel, personal fees from Magnamed, outside the submitted work; Dr. Ho reports personal fees from Pan‐American Health Organization, outside the submitted work. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. The other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Geneva: WHO; 2023. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed 2023 July 7.
-
- Ranzani OT, Bastos LSL, Gelli JGM, Marchesi JF, Baião F, Hamacher S, et al.. Characterisation of the first 250 000 hospital admissions for COVID-19 in Brazil: a retrospective analysis of nationwide data. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. Apr 1;9(4):407–418. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30560-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants. Geneva: WHO; 2023. Available from: https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants. Accessed 2022 Oct 24.
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

