FAM81A is a postsynaptic protein that regulates the condensation of postsynaptic proteins via liquid-liquid phase separation
- PMID: 38452102
- PMCID: PMC10919877
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002006
FAM81A is a postsynaptic protein that regulates the condensation of postsynaptic proteins via liquid-liquid phase separation
Abstract
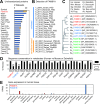
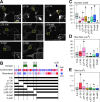
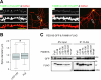
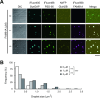
Proteome analyses of the postsynaptic density (PSD), a proteinaceous specialization beneath the postsynaptic membrane of excitatory synapses, have identified several thousands of proteins. While proteins with predictable functions have been well studied, functionally uncharacterized proteins are mostly overlooked. In this study, we conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis of 35 PSD proteome datasets, encompassing a total of 5,869 proteins. Employing a ranking methodology, we identified 97 proteins that remain inadequately characterized. From this selection, we focused our detailed analysis on the highest-ranked protein, FAM81A. FAM81A interacts with PSD proteins, including PSD-95, SynGAP, and NMDA receptors, and promotes liquid-liquid phase separation of those proteins in cultured cells or in vitro. Down-regulation of FAM81A in cultured neurons causes a decrease in the size of PSD-95 puncta and the frequency of neuronal firing. Our findings suggest that FAM81A plays a crucial role in facilitating the interaction and assembly of proteins within the PSD, and its presence is important for maintaining normal synaptic function. Additionally, our methodology underscores the necessity for further characterization of numerous synaptic proteins that still lack comprehensive understanding.
Copyright: © 2024 Kaizuka et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Anchoring high concentrations of SynGAP at postsynaptic densities via liquid-liquid phase separation.Small GTPases. 2019 Jul;10(4):296-304. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1320350. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28524815 Free PMC article.
-
FAM81A protein, a novel component of the postsynaptic density in adult brain.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Apr 23;699:122-126. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.02.003. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30735723 Free PMC article.
-
Essential contribution of the ligand-binding beta B/beta C loop of PDZ1 and PDZ2 in the regulation of postsynaptic clustering, scaffolding, and localization of postsynaptic density-95.J Neurosci. 2006 Jan 18;26(3):763-74. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2489-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16421296 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranslational Modifications Regulate the Postsynaptic Localization of PSD-95.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Apr;54(3):1759-1776. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9745-1. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26884267 Review.
-
Phase separation as a mechanism for assembling dynamic postsynaptic density signalling complexes.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2019 Aug;57:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.12.001. Epub 2018 Dec 29. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30599311 Review.
Cited by
-
Remodeling of the postsynaptic proteome in male mice and marmosets during synapse development.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 28;15(1):2496. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46529-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38548776 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

