The S1 spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 upregulates the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway in DC-SIGN-expressing THP-1 cells
- PMID: 38453000
- PMCID: PMC10951521
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cstres.2024.03.002
The S1 spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 upregulates the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway in DC-SIGN-expressing THP-1 cells
Abstract
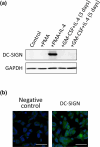
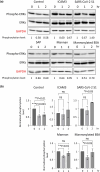
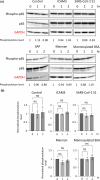
Dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and other antigen-presenting cells express various C-type lectin receptors that function to recognize the glycans associated with pathogens. The dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing non-integrin (DC-SIGN) binds various pathogens such as HIV glycoprotein 120, the Ebola glycoprotein, hemagglutinin, and the dengue virus glycoprotein in addition to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and also triggers antigen-presenting cell endocytosis and immune escape from systemic infections. Many studies on the binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with glycans have been published, but the underlying mechanism by which intracellular signaling occurs remains unclear. In this study, we report that the S1 spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) in THP-1 cells, a DC-SIGN-expressing human monocytic leukemic cell line. On the other hand, the phosphorylation level of NF-κB remained unchanged under the same conditions. These data suggest that the major cell signaling pathway regulated by the S1 spike protein is the ERK pathway, which is superior to the NF-κB pathway in these DC-SIGN-expressing THP-1 cells and may contribute to immune hyperactivation in SARS-CoV-2 infections. Additionally, several glycans such as mannans, mannosylated bovine serum albumin, the serum amyloid beta protein, and intracellular adhesion molecule 3 suppressed ERK phosphorylation, suggesting that these molecules are target molecules for SARS-CoV-2 infection by suppressing immune hyperactivation that occurs in the ERK signaling pathway.
Keywords: DC-SIGN; Dendritic cell; ERK; NF-κB; SARS-CoV-2 S1.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN) is a cellular receptor for delta inulin adjuvant.Immunol Cell Biol. 2024 Aug;102(7):593-604. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12774. Epub 2024 May 17. Immunol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38757764 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 binds Tollip and activates pro-inflammatory pathways while downregulating interferon-α and interferon-γ receptors.mBio. 2025 Aug 13;16(8):e0107125. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01071-25. Epub 2025 Jun 25. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40558091 Free PMC article.
-
Human surfactant protein D facilitates SARS-CoV-2 pseudotype binding and entry in DC-SIGN expressing cells, and downregulates spike protein induced inflammation.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 28;13:960733. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.960733. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35967323 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inference of differential kinase interaction networks with KINference.Bioinformatics. 2025 Jul 1;41(7):btaf349. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf349. Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40579228 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane protein CRISPR screen identifies RPSA as an essential host factor for porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication.J Virol. 2025 Aug 19;99(8):e0064925. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00649-25. Epub 2025 Jul 30. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40736249 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

