[Value of CT Quantitative Parameters in Prediction of Pathological Types of Lung Ground Glass Nodules]
- PMID: 38453443
- PMCID: PMC10918243
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2024.102.09
[Value of CT Quantitative Parameters in Prediction of Pathological Types of Lung Ground Glass Nodules]
Abstract
Background: The pathological types of lung ground glass nodules (GGNs) show great significance to the clinical treatment. This study was aimed to predict pathological types of GGNs based on computed tomography (CT) quantitative parameters.
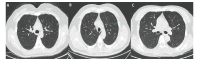
Methods: 389 GGNs confirmed by postoperative pathology were selected, including 138 cases of precursor glandular lesions [atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) and adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS)], 109 cases of microinvasive adenocarcinoma (MIA) and 142 cases of invasive adenocarcinoma (IAC). The morphological characteristics of nodules were evaluated subjectively by radiologist, as well as artificial intelligence (AI).
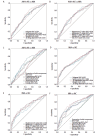
Results: In the subjective CT signs, the maximum diameter of nodule and the frequency of spiculation, lobulation and pleural traction increased from AAH+AIS, MIA to IAC. In the AI quantitative parameters, parameters related to size and CT value, proportion of solid component, energy and entropy increased from AAH+AIS, MIA to IAC. There was no significant difference between AI quantitative parameters and the subjective CT signs for distinguishing the pathological types of GGNs.
Conclusions: AI quantitative parameters were valuable in distinguishing the pathological types of GGNs.
【中文题目:CT定量参数预测肺磨玻璃结节病理类型 的价值】 【中文摘要:背景与目的 肺磨玻璃结节(ground glass nodules, GGNs)的病理类型对临床治疗方案的选择具有十分重要的意义,本研究旨在探讨主观计算机断层扫描(computed tomography, CT)影像学征象及人工智能定量参数在预测GGNs病理类型中的价值。方法 回顾性分析389例病理明确诊断的GGNs,其中,前驱腺体病变[包括非典型瘤样增生(atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, AAH)、原位腺癌(adenocarcinoma in situ, AIS)]138例,微浸润腺癌(microinvasive adenocarcinoma, MIA)109例,浸润性腺癌(invasive adenocarcinoma, IAC)142例。对结节的影像形态学特征进行主观评价,并利用肺结节人工智能系统自动获得定量参数。结果 在主观CT影像学征象中,AAH+AIS、MIA和IAC组间结节最大径及毛刺征、分叶征、胸膜牵拉征出现的频率随病理级别增高而增加;在人工智能定量参数中,结节大小相关参数、CT值相关参数、实性占比、能量及熵随病理级别增高而增加。通过多因素Logistic逐步回归分析,人工智能定量参数在区分GGNs的病理类型中不亚于主观CT影像学征象。结论 人工智能定量参数对区分GGNs的病理类型有一定的价值。 】 【中文关键词:肺肿瘤;磨玻璃结节;病理类型;计算机断层扫描】.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Ground glass nodules; Lung neoplasms; Pathological type.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical