Pharmacologic Characterization of Substituted Nitazenes at μ, κ, and Δ Opioid Receptors Suggests High Potential for Toxicity
- PMID: 38453524
- PMCID: PMC11026150
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.123.002052
Pharmacologic Characterization of Substituted Nitazenes at μ, κ, and Δ Opioid Receptors Suggests High Potential for Toxicity
Abstract
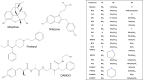
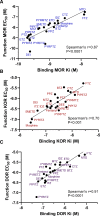
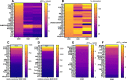
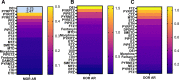
The benzimidazole opioids (substituted nitazenes) are highly potent μ opiod receptor (MOR) agonists with heroin- or fentanyl-like effects. These compounds have caused hospitalizations and fatal overdoses. We characterized the in vitro pharmacology and structure-activity relationships of 19 nitazenes with substitutions at three positions of the benzimidazole core. Affinities were assessed using agonist radioligand binding assays at human μ, κ, and Δ opioid receptors (MOR, KOR, and DOR, respectively) heterologously expressed in CHO cells. Notably, for MOR binding, nine substituted nitazenes had significantly higher affinities than fentanyl including N-pyrrolidino etonitazene, N-pyrrilidino isonitazene, and N-desethyl isotonitazene; 13 had subnanomolar affinities. Only metodesnitazene and flunitazene had significantly lower affinities than fentanyl. Affinities for the substituted nitazenes at KOR and DOR relative to MOR were 46- to 2580-fold and 180- to 1280-fold lower, respectively. Functional activities were assessed using [35S]GTPγS binding assays. Four nitazenes had subnanomolar potencies at MOR: N-pyrrolidino etonitazene, N-pyrrilidino isonitazene, N-pyrrilidino protonitazene and N-desethyl isotonitazene. Ten substituted nitazenes had significantly higher potencies than fentanyl. All tested nitazenes were full MOR agonists. Potencies at KOR and DOR relative to MOR were 7.3- to 7920-fold and 24- to 9400-fold lower, respectively. Thus, many of these compounds are high affinity/high potency MOR agonists with elevated potential to elicit toxicity and overdose at low doses. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Substituted nitazenes are a growing public health threat. Although the 19 nitazenes tested vary in their opioid receptor pharmacology, a number are very high affinity, high potency, and high efficacy compounds- higher than fentanyl. Their pharmacology suggests high potential for harm.
U.S. Government work not protected by U.S. copyright.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad FB, Cisewski JA, Rossen LM, Sutton P (2024) Provisional drug overdose death counts. National Center for Health Statistics.
-
- Björkman S, Wada DR, Stanski DR, Ebling WF (1994) Comparative physiological pharmacokinetics of fentanyl and alfentanil in rats and humans based on parametric single-tissue models. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 22:381–410. - PubMed
-
- Calello DP, Aldy K, Jefri M, Nguyen TT, Krotulski A, Logan B, Brent J, Wax P, Walton S, Manini AF; ToxIC Fentalog Study Group (2022) Identification of a novel opioid, N-piperidinyl etonitazene (etonitazepipne), in patients with suspected opioid overdose. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 60:1067–1069. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
