Two acute kidney injury episodes after ICI therapy: a case report
- PMID: 38453804
- PMCID: PMC11444024
- DOI: 10.1007/s13730-024-00855-5
Two acute kidney injury episodes after ICI therapy: a case report
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Two acute kidney injury episodes after ICI therapy: a case report.CEN Case Rep. 2024 Oct;13(5):416-418. doi: 10.1007/s13730-024-00869-z. CEN Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38656748 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
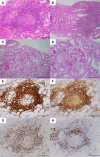
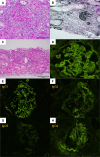
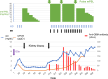
A 74-year-old Japanese male with lung squamous cell carcinoma received his first dose of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs): ipilimumab and nivolumab. He developed acute kidney injury (AKI) and was admitted to our department. We diagnosed kidney immune-related adverse effects (irAE), and a kidney biopsy revealed acute tubulointerstitial nephritis. We started oral prednisolone (PSL) and his AKI immediately improved. The patient maintained stable findings after PSL was tapered off. However, seven months after the ICI administration, he developed rapid progressive glomerular nephritis and was admitted to our department again. The second kidney biopsy showed findings consistent with anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis. Although the patient was treated with pulse methylprednisolone followed by oral PSL and plasma exchange, he became dependent on maintenance hemodialysis. To our knowledge, no case report has described two different types of biopsy-proven nephritis. In cases of suspected relapsing kidney irAEs, both a relapse of previous nephritis and the development of another type of nephritis should be considered.
Keywords: Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis; Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease; Immune-related adverse events.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Japanese Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors have declared no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histological diagnosis of immune checkpoint inhibitor induced acute renal injury in patients with metastatic melanoma: a retrospective case series report.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Sep 7;21(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02044-9. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32894101 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (nivolumab)-associated kidney injury and the importance of recognizing concomitant medications known to cause acute tubulointerstitial nephritis: a case report.BMC Nephrol. 2018 Feb 27;19(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-0848-y. BMC Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29486725 Free PMC article.
-
Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis and IgM deposits on glomerular capillary walls after immunotherapy with nivolumab for metastatic renal cell carcinoma.CEN Case Rep. 2020 Feb;9(1):48-54. doi: 10.1007/s13730-019-00424-1. Epub 2019 Oct 11. CEN Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 31605271 Free PMC article.
-
The Analysis of Renal Infiltrating Cells in Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis Induced by Anti-PD-1 Antibodies: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Intern Med. 2018 Nov 1;57(21):3135-3139. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0444-17. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29877267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated nephritis-treatment standard.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024 Oct 30;39(11):1785-1798. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfae184. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024. PMID: 39138117 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

