Glial-restricted precursors stimulate endogenous cytogenesis and effectively recover emotional deficits in a model of cytogenesis ablation
- PMID: 38454085
- PMCID: PMC11632613
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-024-02490-z
Glial-restricted precursors stimulate endogenous cytogenesis and effectively recover emotional deficits in a model of cytogenesis ablation
Abstract
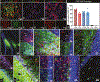
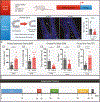
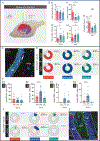
Adult cytogenesis, the continuous generation of newly-born neurons (neurogenesis) and glial cells (gliogenesis) throughout life, is highly impaired in several neuropsychiatric disorders, such as Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), impacting negatively on cognitive and emotional domains. Despite playing a critical role in brain homeostasis, the importance of gliogenesis has been overlooked, both in healthy and diseased states. To examine the role of newly formed glia, we transplanted Glial Restricted Precursors (GRPs) into the adult hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG), or injected their secreted factors (secretome), into a previously validated transgenic GFAP-tk rat line, in which cytogenesis is transiently compromised. We explored the long-term effects of both treatments on physiological and behavioral outcomes. Grafted GRPs reversed anxiety-like deficits and demonstrated an antidepressant-like effect, while the secretome promoted recovery of only anxiety-like behavior. Furthermore, GRPs elicited a recovery of neurogenic and gliogenic levels in the ventral DG, highlighting the unique involvement of these cells in the regulation of brain cytogenesis. Both GRPs and their secretome induced significant alterations in the DG proteome, directly influencing proteins and pathways related to cytogenesis, regulation of neural plasticity and neuronal development. With this work, we demonstrate a valuable and specific contribution of glial progenitors to normalizing gliogenic levels, rescuing neurogenesis and, importantly, promoting recovery of emotional deficits characteristic of disorders such as MDD.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Glial-Restricted Precursors stimulate endogenous cytogenesis and effectively recover emotional deficits in a model of cytogenesis ablation.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 31:rs.3.rs-2747462. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2747462/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Jul;29(7):2185-2198. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02490-z. PMID: 37034743 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Glial-Restricted Precursors stimulate endogenous cytogenesis and effectively recover emotional deficits in a model of cytogenesis ablation.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 31:rs.3.rs-2747462. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2747462/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Jul;29(7):2185-2198. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02490-z. PMID: 37034743 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Increased dentate neurogenesis after grafting of glial restricted progenitors or neural stem cells in the aging hippocampus.Stem Cells. 2007 Aug;25(8):2104-17. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2006-0726. Epub 2007 May 17. Stem Cells. 2007. PMID: 17510219
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein-expressing neural progenitors give rise to immature neurons via early intermediate progenitors expressing both glial fibrillary acidic protein and neuronal markers in the adult hippocampus.Neuroscience. 2010 Mar 10;166(1):241-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.12.026. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20026190
-
Early Life Events and Maturation of the Dentate Gyrus: Implications for Neurons and Glial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 12;23(8):4261. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084261. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult brain cytogenesis in the context of mood disorders: From neurogenesis to the emergent role of gliogenesis.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Dec;131:411-428. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.09.030. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 34555383 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic stress and cytogenesis ablation disrupt hippocampal neuron connectivity, with fluoxetine restoring function with sex-specific effects.Neurobiol Stress. 2025 Jul 7;37:100743. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2025.100743. eCollection 2025 Jul. Neurobiol Stress. 2025. PMID: 40686530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Björk-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, et al. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 1998;4:1313–7. - PubMed
-
- Lucassen PJ, Fitzsimons CP, Salta E, Maletic-Savatic M. Adult neurogenesis, human after all (again): Classic, optimized, and future approaches. Behav Brain Res 2020;381:112458. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

