Direct TAMRA-dUTP labeling of M. tuberculosis genes using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)
- PMID: 38454089
- PMCID: PMC10920756
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-55289-x
Direct TAMRA-dUTP labeling of M. tuberculosis genes using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)
Abstract
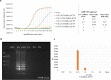
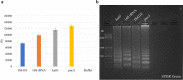
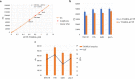
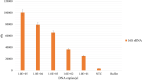
Fluorescent molecule-based direct labeling of amplified DNA is a sensitive method employed across diverse DNA detection and diagnostics systems. However, using pre-labeled primers only allows for the attachment of a single fluorophore to each DNA strand and any modifications of the system are less flexible, requiring new sets of primers. As an alternative, direct labeling of amplified products with modified nucleotides is available, but still poorly characterized. To address these limitations, we sought a direct and adaptable approach to label amplicons produced through Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), using labeled nucleotides (dUTPs) rather than primers. The focus of this study was the development and examination of a direct labeling technique of specific genes, including those associated with drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. We used 5-(3-Aminoallyl)-2'-deoxyuridine-5'triphosphate, tagged with 5/6-TAMRA (TAMRA-dUTP) for labeling LAMP amplicons during the amplification process and characterized amplification and incorporation efficiency. The optimal TAMRA-dUTP concentration was first determined based on amplification efficiency (0.5% to total dNTPs). Higher concentrations of modified nucleotides reduced or completely inhibited the amplification yield. Target size also showed to be determinant to the success of amplification, as longer sequences showed lower amplification rates, thus less TAMRA incorporated amplicons. Finally, we were able to successfully amplify all four M. tuberculosis target genes using LAMP and TAMRA-modified dUTPs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

